Home > Press > New technology aiming to improve trueness in the piezoelectric microscopy characterization of ceramic materials
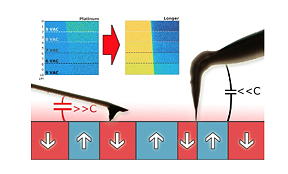 |
| Side view of the two types of AFM probes used. The one at the right is a ultra- long tip which diminish the electrostatic interaction between the cantilever and the sample. Compared to the standard tip-which is images at the right side, the taller tip provides a cleaner piezoresponse signal in order to acquire the piezoelectric response of the material. |
Abstract:
A team of researchers from ICMAB has proved that unconventional AFM probes are suitable
to acquire a trueness piezoelectric signal in Piezoresponse Force Microscopy. The work
entitles “Diminish electrostatic in piezoresponse force microscopy through longer or
ultra-stiff tips” published in the prestigious scientific journal Applied Surface
Science( https://authors.elsevier.com/a/1WNqWcXa~oZkP )
New technology aiming to improve trueness in the piezoelectric microscopy characterization of ceramic materials
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on January 26th, 2018Piezoresponse Force Microscopy is a strongly used characterization technique in the world
of piezoelectrics. Each year almost 300 manuscripts included this technique in their
research, while piezoelectric community publishes more than 5000 papers yearly.
In this work researchers test almost every single AFM conductive probe available in the
market using a novel method that quantifies the electrostatic contribution in their
measurements. The method relies into solving the mathematical expression called
“correlation function” that describes the mathematical operations that a lock-in amplifier
performs to acquire the signals. After the theoretical description, the same sample is studies
with different AFM tips available in the market, through the use of two distinct type of tests.
In the first test, the researchers increment the piezoelectric signal, while maintaining
constant the electrostatic contribution. By doing this, the mount of signal coming from
piezoelectricity increases, and hence, the changes in the final results a dramatically different.
From this test, it is found that longer tips provide the cleaner signal from the overall set of
probes used. These results are confirmed through the use of independent experiments that
corroborates the first results.
The implementation of this solution to the worldwide scientific community is immediate and
can be used in absolutely any AFM manufacturer, which expands the importance and
implications of this research.
####
Contacts:
Andres Gomez
ICMAB-CSIC, Campus UAB
Phone: 677602367
Fax: 677602367
Copyright © Campus de la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








