Home > Press > Enhancing the quantum sensing capabilities of diamond: Shooting electrons at diamonds can introduce quantum sensors into them
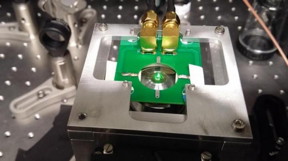 |
| This photo shows a diamond sample illuminated by green light in home-built microscope. The sample is placed on a special mount, within a printed circuit board, used to deliver microwaves which allow quantum manipulations and magnetic sensing with the NVs. CREDIT (Credit: Yoav Romach) |
Abstract:
Researchers have discovered that dense ensembles of quantum spins can be created in diamond with high resolution using an electron microscopes, paving the way for enhanced sensors and resources for quantum technologies.
Enhancing the quantum sensing capabilities of diamond: Shooting electrons at diamonds can introduce quantum sensors into them
Jerusalem, Israel | Posted on November 24th, 2017Diamonds are made of carbon atoms in a crystalline structure, but if a carbon atom is replaced with another type of atom, this will result in a lattice defect. One such defect is the Nitrogen-Vacancy (NV), where one carbon atom is replaced by a nitrogen atom, and its neighbor is missing (an empty space remains in its place).
If this defect is illuminated with a green laser, in response it will emit red light (fluoresce) with an interesting feature: its intensity varies depending on the magnetic properties in the environment. This unique feature makes the NV center particularly useful for measuring magnetic fields, magnetic imaging (MRI), and quantum computing and information.
In order to produce optimal magnetic detectors, the density of these defects should be increased without increasing environmental noise and damaging the diamond properties.
Now, scientists from the research group of Nir Bar-Gill at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem's Racah Institute of Physics and Department of Applied Physics, in cooperation with Prof. Eyal Buks of the Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, have shown that ultra-high densities of NV centers can be obtained by a simple process of using electron beams to kick carbon atoms out of the lattice.
This work, published in the scientific journal Applied Physics Letters, is a continuation of previous work in the field, and demonstrates an improvement in the densities of NV centers in a variety of diamond types. The irradiation is performed using an electron beam microscope (Transmission Electron Microscope or TEM), which has been specifically converted for this purpose. The availability of this device in nanotechnology centers in many universities in Israel and around the world enables this process with high spatial accuracy, quickly and simply.
The enhanced densities of the NV color centers obtained, while maintaining their unique quantum properties, foreshadow future improvements in the sensitivity of diamond magnetic measurements, as well as promising directions in the study of solid state physics and quantum information theory.
Nitrogen Vacancy (NV) color centers exhibit remarkable and unique properties, including long coherence times at room temperature (~ ms), optical initialization and readout, and coherent microwave control.
"This work is an important stepping stone toward utilizing NV centers in diamond as resources for quantum technologies, such as enhanced sensing, quantum simulation and potentially quantum information processing", said Bar-Gill, an Assistant Professor in the Dept. of Applied Physics and Racah Institute of Physics at the Hebrew University, where he founded the Quantum Information, Simulation and Sensing lab.
"What is special about our approach is that it's very simple and straightforward," said Hebrew University researcher Dima Farfurnik. "You get sufficiently high NV concentrations that are appropriate for many applications with a simple procedure that can be done in-house."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dov Smith
972-258-82844
Copyright © The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








