Home > Press > Rice University chemists make laser-induced graphene from wood
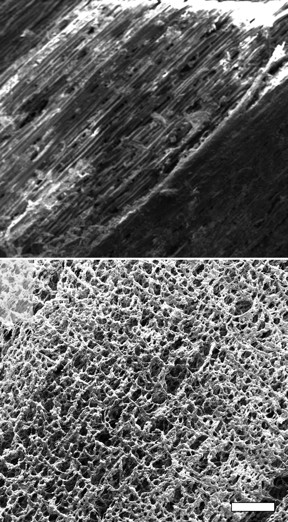 |
| Scanning electron microscope images show pristine pine at top and laser-induced graphene on pine (P-LIG) produced at Rice University at bottom. The scale bar is about 500 micrometers. (Credit: Tour Group/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Rice University scientists have made wood into an electrical conductor by turning its surface into graphene.
A video shows two planks of laser-induced graphene on pine fashioned into catalysts for electrolysis at Rice University. Bubbles from the electrode on the left are hydrogen, and on the right, oxygen. (Credit: Tour Group/Rice University)
Rice University chemists make laser-induced graphene from wood
Houston, TX | Posted on July 31st, 2017Rice chemist James Tour and his colleagues used a laser to blacken a thin film pattern onto a block of pine. The pattern is laser-induced graphene (LIG), a form of the atom-thin carbon material discovered at Rice in 2014.
"It's a union of the archaic with the newest nanomaterial into a single composite structure," Tour said.
The discovery is detailed this month in Advanced Materials.
Previous iterations of LIG were made by heating the surface of a sheet of polyimide, an inexpensive plastic, with a laser. Rather than a flat sheet of hexagonal carbon atoms, LIG is a foam of graphene sheets with one edge attached to the underlying surface and chemically active edges exposed to the air.
Not just any polyimide would produce LIG, and some woods are preferred over others, Tour said. The research team led by Rice graduate students Ruquan Ye and Yieu Chyan tried birch and oak, but found that pine's cross-linked lignocellulose structure made it better for the production of high-quality graphene than woods with a lower lignin content. Lignin is the complex organic polymer that forms rigid cell walls in wood.
Ye said turning wood into graphene opens new avenues for the synthesis of LIG from nonpolyimide materials. "For some applications, such as three-dimensional graphene printing, polyimide may not be an ideal substrate," he said. "In addition, wood is abundant and renewable."
As with polyimide, the process takes place with a standard industrial laser at room temperature and pressure and in an inert argon or hydrogen atmosphere. Without oxygen, heat from the laser doesn't burn the pine but transforms the surface into wrinkled flakes of graphene foam bound to the wood surface. Changing the laser power also changed the chemical composition and thermal stability of the resulting LIG. At 70 percent power, the laser produced the highest quality of what they dubbed "P-LIG," where the P stands for “pine.”
The lab took its discovery a step further by turning P-LIG into electrodes for splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen and supercapacitors for energy storage. For the former, they deposited layers of cobalt and phosphorus or nickel and iron onto P-LIG to make a pair of electrocatalysts with high surface areas that proved to be durable and effective.
Depositing polyaniline onto P-LIG turned it into an energy-storing supercapacitor that had usable performance metrics, Tour said.
"There are more applications to explore," Ye said. "For example, we could use P-LIG in the integration of solar energy for photosynthesis. We believe this discovery will inspire scientists to think about how we could engineer the natural resources that surround us into better-functioning materials."
Tour saw a more immediate environmental benefit from biodegradable electronics.
"Graphene is a thin sheet of a naturally occurring mineral, graphite, so we would be sending it back to the ground from which it came along with the wood platform instead of to a landfill full of electronics parts."
Co-authors of the paper are Rice graduate students Jibo Zhang and Yilun Li; Xiao Han, who has a complimentary appointment at Rice and is a graduate student at Beihang University, Beijing, China; and Rice research scientist Carter Kittrell. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice.
The Air Force Office of Scientific Research Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative and the NSF Nanosystems Engineering Research Center for Nanotechnology-Enabled Water Treatment supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,879 undergraduates and 2,861 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Rice U. chemists create 3-D printed graphene foam:
Rice U. chemists create 3-D printed graphene foam:
![]() Zap! Graphene is bad news for bacteria:
Zap! Graphene is bad news for bacteria:
![]() Gas gives laser-induced graphene super properties:
Gas gives laser-induced graphene super properties:
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








