Home > Press > Photonics breakthough paving the way for improved wireless communication systems: The work could bolster the wireless revolution underway with efficiencies several orders of magnitude
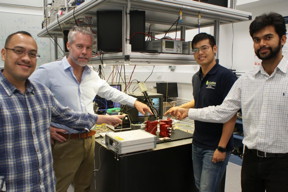 |
| Researchers David Marpaung, Benjamin Eggleton, Yang Liu and Amol Choudhary pointing at a thumbnail-size chip being evaluated in the broadband microwave testbed, inside the Sydney Nanoscience Hub. CREDIT University of Sydney |
Abstract:
Researchers from the ARC Centre for Ultrahigh bandwidth Devices for Optical Systems (CUDOS) in the University of Sydney's Australian Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology have made a breakthrough achieving radio frequency signal control at sub-nanosecond time scales on a chip-scale optical device.
Photonics breakthough paving the way for improved wireless communication systems: The work could bolster the wireless revolution underway with efficiencies several orders of magnitude
Sydney, Australia | Posted on April 5th, 2017Radio frequency (RF) is a particular range of electromagnetic wave frequencies, widely used for communications and radar signals. The work should impact the current wireless revolution.
The breakthrough was detailed today in the high-impact journal Optica.
CUDOS and School of Physics PhD candidate at the University of Sydney, lead author Yang Liu, said the new research that could unlock the bandwidth bottleneck faced by wireless networks worldwide was undertaken at the headquarters of the Australian Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology (AINST), the $150m Sydney Nanoscience Hub.
"Nowadays, there are 10 billion mobile devices connected to the wireless network (reported by Cisco last year) and all require bandwidth and capacity," Mr Liu said.
"By creating very fast tunable delay lines on chip, one eventually can provide broader bandwidth instantaneously to more users.
"The ability of rapidly controlling RF signal is a crucial performance for applications in both our daily life and defence.
"For example, to reduce power consumption and maximize reception range for future mobile communications, RF signals need to achieve directional and fast distributions to different cellular users from information centres, instead of spreading signal energy in all directions."
The lack of the high tuning speed in current RF technique in modern communications and defence, has motivated the development of solutions on a compact optical platform.
These optical counterparts had been typically limited in performance by a low tuning speed on the order of milliseconds (1/1000 of a second) offered by on-chip heaters, with side effects of fabrication complexity and power consumption.
"To circumvent these problems, we developed a simple technique based on optical control with response time faster than one nanosecond: a billionth of a second -- this is a million times faster than thermal heating," said Mr Liu.
CUDOS Director and co-author Professor Benjamin Eggleton, who also heads the Nanoscale Photonics Circuits AINST flagship, said the technology would not only be important for building more efficient radars to detect enemy attacks but would also make significant improvements for everyone.
"Such a system will be crucial not only to safeguard our defence capabilities, it will also help foster the so-called wireless revolution -- where more and more devices are connected to the wireless network," Professor Eggleton said.
"This includes the internet of things, fifth generation (5G) communications, and smart home and smart cities.
"Silicon photonics, the technology that underpins this advance, is progressing very quickly, finding applications in datacentres right now.
"We expect the applications of this work will happen within a decade in order to provide a solution to the wireless bandwdith problem.
"We are currently working on the more advanced silicon devices that are highly integrated and can be used in small mobile devices," Professor Eggleton said.
By optically varying the control signal at gigahertz speeds, the time delay of the RF signal can be amplified and switched at the same speed.
Mr Liu and fellow researchers Dr Amol Choudhary, Dr David Marpaung and Professor Eggleton achieved this on an integrated photonic chip, paving the way towards ultrafast and reconfigurable on-chip RF systems with unmatched advantages in compactness, low power consumption, low fabrication complexity, flexibility and compatibility with existing RF functionalities.
###
The research builds on research supported by the Australian Research Council through CUDOS, a Centre of Excellence headquartered at the University of Sydney.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Vivienne Reiner
61-293-512-390
Copyright © University of Sydney
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








