Home > Press > Rice U. refines filters for greener natural gas: New study defines best materials for carbon capture, methane selectivity
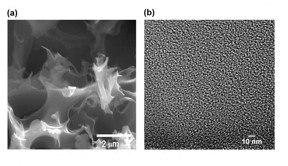 |
| A scanning electron microscope image, left, and a high-resolution transmission electron microscope image show an activated, sulfur-containing porous carbon sample. The material created at Rice University can be tuned to balance carbon dioxide sequestration and methane selectivity. CREDIT Barron Research Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
Natural gas producers want to draw all the methane they can from a well while sequestering as much carbon dioxide as possible, and could use filters that optimize either carbon capture or methane flow. No single filter will do both, but thanks to Rice University scientists, they now know how to fine-tune sorbents for their needs.
Rice U. refines filters for greener natural gas: New study defines best materials for carbon capture, methane selectivity
Houston, TX | Posted on March 23rd, 2017Subtle adjustments in the manufacture of a polymer-based carbon sorbent make it the best-known material either for capturing the greenhouse gas or balancing carbon capture with methane selectivity, according to Rice chemist Andrew Barron.
The specifics are in a paper this month by Barron and Rice research scientist Saunab Ghosh in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Sustainable Energy and Fuels.
"The challenge is to capture as much carbon as possible while allowing methane to flow through at typical wellhead pressures," Barron said. "We've defined the parameters in a map that gives industry the best set of options to date."
Previous work by the lab determined that carbon filters maxed out their capture ability with a surface area of 2,800 square meters per gram and a pore volume of 1.35 cubic centimeters per gram. They also discovered the best carbon capture material didn't achieve the best trade-off between carbon and methane selectivity. With the new work, they know how to tune the material for one or the other, Barron said.
"The traditional approach has been to make materials with ever-increasing pore volume and relate this to a better adsorbent; however, it appears to be a little more subtle," he said.
The lab made its latest filters by heating a polymer precursor and then treating it with a chemical activation reagent of potassium, oxygen and hydrogen, aka KOH. When the polymer is baked with KOH at temperatures over 500 degrees Celsius (932 degrees Fahrenheit), it becomes a highly porous filter, full of nanoscale channels that can trap carbon.
The ratio of KOH to polymer during processing turned out to be the critical factor in determining the final filter's characteristics. Making filters with a 3-to-1 ratio of KOH to polymer gave it a surface area of 2,700 square meters per gram and maximized carbon dioxide uptake under pressures of 5 to 30 bar. (One bar is slightly less than the average atmospheric pressure at sea level.)
Filters made with a 2-to-1 ratio of KOH to polymer had less surface area -- 2,200 square meters per gram -- and a lower pore volume. That resulted in the optimum combination of carbon dioxide uptake and methane selectivity.
The size of the pores was critical as well. Filters with maximum carbon uptake had the largest fraction of pores smaller than 2 nanometers. Bigger pores were better for methane selectivity.
"It appears that total pore volume is less important than the relative quantity of pores at specific sizes," Barron said. "Our goal was to create a guide for researchers and industry to design better materials.
"Not only can these materials be used for carbon dioxide separation from natural gas, but they are also models for carbon dioxide sequestration in a natural resource. This is the future direction of our research."
###
Barron is the Charles W. Duncan Jr.-Welch Professor of Chemistry and a professor of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice.
Apache Corp., the Welsh Government SÍr Cymru Program and the Robert A. Welch Foundation supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,879 undergraduates and 2,861 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








