Home > Press > Discovery in new material raises questions about theoretical models of superconductivity
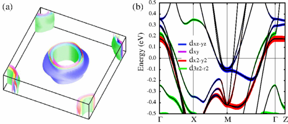 |
| (a) Calculated 3D Fermi surface of CaKFe 4 As 4 (b) Band dispersion along the key symmetry directions with respective orbital contributions marked by color-coded outlines. Copyright American Physical Society, used with permission |
Abstract:
The U.S. Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory has successfully created the first pure, single-crystal sample of a new iron arsenide superconductor, CaKFe4As4, and studies of this material have called into question some long-standing theoretical models of superconductivity.
Discovery in new material raises questions about theoretical models of superconductivity
Ames, IA | Posted on March 13th, 2017The material is notable for having the high superconducting temperature of 35K without the need for small amounts of additional elements (such as cobalt or nickel), called dopants.
"That is important because dopants, that were previously used to induce superconductivity, also interfere with superconductivity and other important physical properties of materials" said Adam Kaminski, Ames Laboratory scientist and professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Iowa State University. "This material gave us an excellent opportunity to study superconductivity in pristine samples without the interference of dopants."
Using high resolution angle resolved photoemission spectroscopy and density functional theory, researchers were able to measure the superconducting gap in areas of the momentum space that were previously inaccessible in other materials, and found that their results contradicted the widely accepted antiferromagnetic fluctuation model.
"Our data obtained from samples of pristine iron-arsenic superconductor represents a big deviation from previous studies of doped samples and questions some well-established theories," said Kaminski. "It means that the predictions of previous models are at only partly valid, and there many aspects that are not completely understood. What our work has achieved is to create a new clean avenue of research, towards finding a general model to explain the behavior of these novel superconductors."
The research was conducted at Ames Laboratory and Institut fur Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr Universität Bochum, Germany.
The work was supported by the U.S. Department of Department of Energy's Office of Science.
####
About Ames Laboratory
Ames Laboratory is a U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science national laboratory operated by Iowa State University. Ames Laboratory creates innovative materials, technologies and energy solutions. We use our expertise, unique capabilities and interdisciplinary collaborations to solve global problems.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Laura Millsaps
Copyright © Ames Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








