Home > Press > UCLA physicists map the atomic structure of an alloy: Researchers measured the coordinates of more than 23,000 atoms in a technologically important material
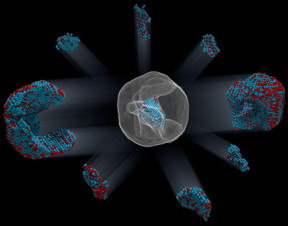 |
| Identification of the 3-D coordinates of 6,569 iron and 16,627 platinum atoms in an iron-platinum nanoparticle to correlate 3-D atomic arrangements with material properties at the single-atom level. CREDIT Courtesy of Colin Ophus and Florian Nickel |
Abstract:
In the world of the very tiny, perfection is rare: virtually all materials have defects on the atomic level. These imperfections -- missing atoms, atoms of one type swapped for another, and misaligned atoms -- can uniquely determine a material's properties and function. Now, UCLA physicists and collaborators have mapped the coordinates of more than 23,000 individual atoms in a tiny iron-platinum nanoparticle to reveal the material's defects.
UCLA physicists map the atomic structure of an alloy: Researchers measured the coordinates of more than 23,000 atoms in a technologically important material
Los Angeles, CA | Posted on February 3rd, 2017The results demonstrate that the positions of tens of thousands of atoms can be precisely identified and then fed into quantum mechanics calculations to correlate imperfections and defects with material properties at the single-atom level. This research will be published Feb 2. in the journal Nature.
Jianwei (John) Miao, a UCLA professor of physics and astronomy and a member of UCLA's California NanoSystems Institute, led the international team in mapping the atomic-level details of the bimetallic nanoparticle, more than a trillion of which could fit within a grain of sand.
"No one has seen this kind of three-dimensional structural complexity with such detail before," said Miao, who is also a deputy director of the Science and Technology Center on Real-Time Functional Imaging. This new National Science Foundation-funded consortium consists of scientists at UCLA and five other colleges and universities who are using high-resolution imaging to address questions in the physical sciences, life sciences and engineering.
Miao and his team focused on an iron-platinum alloy, a very promising material for next-generation magnetic storage media and permanent magnet applications.
By taking multiple images of the iron-platinum nanoparticle with an advanced electron microscope at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and using powerful reconstruction algorithms developed at UCLA, the researchers determined the precise three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in the nanoparticle.
"For the first time, we can see individual atoms and chemical composition in three dimensions. Everything we look at, it's new," Miao said.
The team identified and located more than 6,500 iron and 16,600 platinum atoms and showed how the atoms are arranged in nine grains, each of which contains different ratios of iron and platinum atoms. Miao and his colleagues showed that atoms closer to the interior of the grains are more regularly arranged than those near the surfaces. They also observed that the interfaces between grains, called grain boundaries, are more disordered.
"Understanding the three-dimensional structures of grain boundaries is a major challenge in materials science because they strongly influence the properties of materials," Miao said. "Now we are able to address this challenge by precisely mapping out the three-dimensional atomic positions at the grain boundaries for the first time."
The researchers then used the three-dimensional coordinates of the atoms as inputs into quantum mechanics calculations to determine the magnetic properties of the iron-platinum nanoparticle. They observed abrupt changes in magnetic properties at the grain boundaries.
"This work makes significant advances in characterization capabilities and expands our fundamental understanding of structure-property relationships, which is expected to find broad applications in physics, chemistry, materials science, nanoscience and nanotechnology," Miao said.
In the future, as the researchers continue to determine the three-dimensional atomic coordinates of more materials, they plan to establish an online databank for the physical sciences, analogous to protein databanks for the biological and life sciences. "Researchers can use this databank to study material properties truly on the single-atom level," Miao said.
Miao and his team also look forward to applying their method called GENFIRE (GENeralized Fourier Iterative Reconstruction) to biological and medical applications. "Our three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm might be useful for imaging like CT scans," Miao said. Compared with conventional reconstruction methods, GENFIRE requires fewer images to compile an accurate three-dimensional structure.
That means that radiation-sensitive objects can be imaged with lower doses of radiation.
###
The study's co-authors include Yongsoo Yang, Rui Xu, AJ Pryor, Li Wu and Jihan Zhou, all at UCLA; Mary Scott, Colin Ophus, and Peter Ercius of Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; Chien-Chun Chen of the National Sun Yat-sen University; Fan Sun and Hao Zeng of the University at Buffalo; Markus Eisenbach and Paul Kent of Oak Ridge National Laboratory; Wolfgang Theis of the University of Birmingham; and Renat Sabirianov of the University of Nebraska Omaha.
This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Basic Energy Sciences (grants DE-SC0010378, DE-AC02--05CH11231 and DE-AC05-00OR22725) as well as the U.S. National Science Foundation's Division of Materials Research (grants DMR-1548924 and DMR-1437263).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Stuart Wolpert
310-206-0511
Copyright © University of California - Los Angeles
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








