Home > Press > Recreating conditions inside stars with compact lasers: Scientists offer a new path to creating the extreme conditions found in stars, using ultra-short laser pulses irradiating nanowires
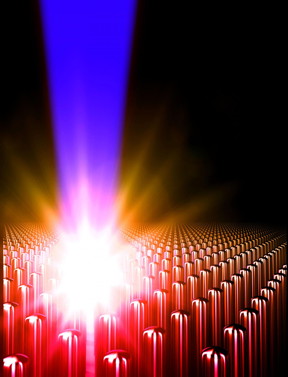 |
| Representation of the creation of ultra-high energy density matter by an intense laser pulse irradiation of an array of aligned nanowires. CREDIT R. Hollinger and A. Beardall |
Abstract:
The energy density contained in the center of a star is higher than we can imagine - many billions of atmospheres, compared with the 1 atmosphere of pressure we live with here on Earth's surface.
Recreating conditions inside stars with compact lasers: Scientists offer a new path to creating the extreme conditions found in stars, using ultra-short laser pulses irradiating nanowires
Ft. Collins, CO | Posted on January 12th, 2017These extreme conditions can only be recreated in the laboratory through fusion experiments with the world's largest lasers, which are the size of stadiums. Now, scientists have conducted an experiment at Colorado State University that offers a new path to creating such extreme conditions, with much smaller, compact lasers that use ultra-short laser pulses irradiating arrays of aligned nanowires.
The experiments, led by University Distinguished Professor Jorge Rocca in the Departments of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Physics, accurately measured how deeply these extreme energies penetrate the nanostructures. These measurements were made by monitoring the characteristic X-rays emitted from the nanowire array, in which the material composition changes with depth.
Numerical models validated by the experiments predict that increasing irradiation intensities to the highest levels made possible by today's ultrafast lasers could generate pressures to surpass those in the center of our sun.
The results, published Jan. 11 in the journal Science Advances, open a path to obtaining unprecedented pressures in the laboratory with compact lasers. The work could open new inquiry into high energy density physics; how highly charged atoms behave in dense plasmas; and how light propagates at ultrahigh pressures, temperatures, and densities.
Creating matter in the ultra-high energy density regime could inform the study of laser-driven fusion - using lasers to drive controlled nuclear fusion reactions - and to further understanding of atomic processes in astrophysical and extreme laboratory environments.
The ability to create ultra-high energy density matter using smaller facilities is thus of great interest for making these extreme plasma regimes more accessible for fundamental studies and applications. One such application is the efficient conversion of optical laser light into bright flashes of X-rays.
The work was a multi-institutional effort led by CSU that included graduate students Clayton Bargsten, Reed Hollinger, Alex Rockwood, and undergraduate David Keiss, all working with Rocca. Also involved were research scientists Vyacheslav Shlyapsev, who worked in modeling, and Yong Wang and Shoujun Wang, all from the same group.
Co-authorship included Maria Gabriela Capeluto from the University of Buenos Aires, and Richard London, Riccardo Tommasini and Jaebum Park from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL). Numerical simulations were conducted by Vural Kaymak and Alexander Pukhov from Heinrich-Heine University in Dusseldorf, using atomic data by Michael Busquet and Marcel Klapisch from Artep, Inc.
###
The research was supported by the High Energy Density Laboratory Plasmas program in Fusion Energy Sciences, Office of Science, in the U.S Department of Energy. It was also aided by a previous grant from the Defense Threat Reduction Agency. The work of the LLNL researchers was performed under the auspices of the U.S Department of Energy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anne Manning
607-592-7387
Copyright © Colorado State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








