Home > Press > First use of graphene to detect cancer cells: System able to detect activity level of single interfaced cell
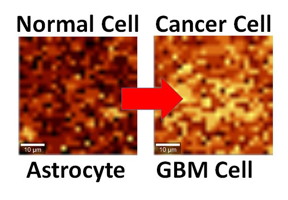 |
| Normal and cancerous brain cells interfaced with graphene show different activity levels under Raman imaging. CREDIT UIC/Vikas Berry |
Abstract:
What can't graphene do? You can scratch "detect cancer" off of that list.
By interfacing brain cells onto graphene, researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago have shown they can differentiate a single hyperactive cancerous cell from a normal cell, pointing the way to developing a simple, noninvasive tool for early cancer diagnosis.
First use of graphene to detect cancer cells: System able to detect activity level of single interfaced cell
Chicago, IL | Posted on December 20th, 2016"This graphene system is able to detect the level of activity of an interfaced cell," says Vikas Berry, associate professor and head of chemical engineering at UIC, who led the research along with Ankit Mehta, assistant professor of clinical neurosurgery in the UIC College of Medicine.
"Graphene is the thinnest known material and is very sensitive to whatever happens on its surface," Berry said. The nanomaterial is composed of a single layer of carbon atoms linked in a hexagonal chicken-wire pattern, and all the atoms share a cloud of electrons moving freely about the surface.
"The cell's interface with graphene rearranges the charge distribution in graphene, which modifies the energy of atomic vibration as detected by Raman spectroscopy," Berry said, referring to a powerful workhorse technique that is routinely used to study graphene.
The atomic vibration energy in graphene's crystal lattice differs depending on whether it's in contact with a cancer cell or a normal cell, Berry said, because the cancer cell's hyperactivity leads to a higher negative charge on its surface and the release of more protons.
"The electric field around the cell pushes away electrons in graphene's electron cloud," he said, which changes the vibration energy of the carbon atoms. The change in vibration energy can be pinpointed by Raman mapping with a resolution of 300 nanometers, he said, allowing characterization of the activity of a single cell.
The study, reported in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, looked at cultured human brain cells, comparing normal astrocytes to their cancerous counterpart, the highly malignant brain tumor glioblastoma multiforme. The technique is now being studied in a mouse model of cancer, with results that are "very promising," Berry said. Experiments with patient biopsies would be further down the road.
"Once a patient has brain tumor surgery, we could use this technique to see if the tumor relapses," Berry said. "For this, we would need a cell sample we could interface with graphene and look to see if cancer cells are still present."
The same technique may also work to differentiate between other types of cells or the activity of cells.
"We may be able to use it with bacteria to quickly see if the strain is Gram-positive or Gram-negative," Berry said. "We may be able to use it to detect sickle cells."
Earlier this year, Berry and other coworkers introduced nanoscale ripples in graphene, causing it to conduct differently in perpendicular directions, useful for electronics. They wrinkled the graphene by draping it over a string of rod-shaped bacteria, then vacuum-shrinking the germs.
"We took the earlier work and sort of flipped it over," Berry said. "Instead of laying graphene on cells, we laid cells on graphene and studied graphene's atomic vibrations."
###
Co-authors on the study are Bijentimala Keisham and Phong Nguyen of UIC chemical engineering and Arron Cole of UIC neurosurgery.
Funding was provided by UIC.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bill Burton
312-996-2269
Copyright © University of Illinois at Chicago
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








