Home > Press > UTSA study describes new minimally invasive device to treat cancer and other illnesses: Medicine diffusion capsule could locally treat multiple ailments and diseases over several weeks
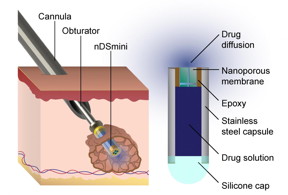 |
| This diagram describes how the device Dr. Hood helped to develop is implanted into a cancerous tumor. CREDIT Lyle Hood/UTSA |
Abstract:
A new study by Lyle Hood, assistant professor of mechanical engineering at The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA), describes a new device that could revolutionize the delivery of medicine to treat cancer as well as a host of other diseases and ailments. Hood developed the device in partnership with Alessandro Grattoni, chair of the Department of Nanomedicine at Houston Methodist Research Institute.
UTSA study describes new minimally invasive device to treat cancer and other illnesses: Medicine diffusion capsule could locally treat multiple ailments and diseases over several weeks
San Antonio, TX | Posted on December 3rd, 2016"The problem with most drug-delivery systems is that you have a specific minimum dosage of medicine that you need to take for it to be effective," Hood said. "There's also a limit to how much of the drug can be present in your system so that it doesn't make you sick."
As a result of these limitations, a person who needs frequent doses of a specific medicine is required to take a pill every day or visit a doctor for injections. Hood's creation negates the need for either of these approaches, because it's a tiny implantable drug delivery system.
"It's an implantable capsule, filled with medicinal fluid that uses about 5000 nanochannels to regulate the rate of release of the medicine," Hood said. "This way, we have the proper amount of drugs in a person's system to be effective, but not so much that they'll harm that person."
The capsule can deliver medicinal doses for several days or a few weeks. According to Hood, it can be used for any kind of ailment that needs a localized delivery over several days or a few weeks. This makes it especially tailored for treating cancer, while a larger version of the device, which was originally created by Grattoni, can treat diseases like HIV for up to a year.
"In HIV treatment, you can bombard the virus with drugs to the point that that person is no longer infectious and shows no symptoms," Hood said. "The danger is that if that person stops taking their drugs, the amount of medicine in his or her system drops below the effective dose and the virus is able to become resistant to the treatments."
The capsule, however, could provide a constant delivery of the HIV-battling drugs to prevent such an outcome. Hood noted it can also be used to deliver cortisone to damaged joints to avoid painful, frequent injections, and possibly even to pursue immunotherapy treatments for cancer patients.
"The idea behind immunotherapy is to deliver a cocktail of immune drugs to call attention to the cancer in a person's body, so the immune system will be inspired to get rid of the cancer itself," he said.
The current prototype of the device is permanent and injected under the skin, but Hood is working with Teja Guda, assistant professor of biomedical engineering, to collaborate on 3-D printing technology to make a new, fully biodegradable iteration of the device that could potentially be swallowed.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Joanna Carver
210-243-4557
Copyright © University of Texas at San Antonio
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








