Home > Press > Controlled electron pulses
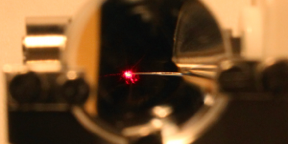 |
| View through a lens: a laser beam strikes a nanotip. (Image: Dr. Michael Förster) |
Abstract:
The discovery of photoemission, the emission of electrons from a material caused by light striking it, was an important element in the history of physics for the development of quantum mechanics. Scientists from the Chair of Laser Physics at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) have successfully measured photoemission from sharp metal needles on a scale never before achieved. The researchers' results have been published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Controlled electron pulses
Nürnberg, Germany | Posted on November 30th, 2016The discovery of photoemission, the emission of electrons from a material caused by light striking it, was an important element in the history of physics for the development of quantum mechanics. Scientists from the Chair of Laser Physics at FAU have successfully measured photoemission from sharp metal needles on a scale never before achieved. The researchers' results have been published in the current issue of the journal Physical Review Letters.
For this two-colour experiment, as they refer to it, the researchers - Dr. Michael Förster, Timo Paschen, Dr. Michael Krüger and Prof. Dr. Peter Hommelhoff - pumped laser pulses with a duration of approximately a nanosecond through a crystal. The crystal combined two photons from the laser pulse. In addition to the strong laser pulse being shone on the crystal, another weak pulse of light with a higher frequency was created. Particularly remarkable was the discovery that the new photons exhibited twice the energy of the original photons. In an interferometer, the FAU scientists separated both colours and determined the direction of vibration, intensity and delay of both pulses.
When the laser pulses meet on the tungsten needle, their energy is concentrated at the vertex of its tip. This limits electron emission to the end of the tip. The researchers observed that, under optimal parameters, they could almost perfectly turn on and off electron emission by controlling the delays between laser pulses. This initially came as a surprise, as light energy (photons) can always be found on the tip; therefore this meant that the relative arrival times of the differently-coloured laser pulses determined whether electrons were or were not emitted.
The researchers came to the idea for this control mechanism by comparing experimental results with calculations by physicists working under Prof. Dr. Joachim Burgdörfer at Technische Universität Wien. They surmised that the electrons could interact with photons from both pulses for emission. This led to two dominant emission paths, but the delay between pulses determined whether these paths would complement or work against each other; emission was either intensified or suppressed in what is known as quantum path interference.
Sharp metal tips have long been used as nearly-punctual electron sources for highest-resolution electron microscopes. Based on the results of this experiment, the researchers hope to create complex electron pulses in the future which could be significant for time-resolved electron microscopy. The experimental results are also of interest for basic research into surface coherence, as the surface of nanostructures can be particularly well controlled and the nanotips produce exceptionally clear measurement signals thanks to their small dimensions.
The renowned journal Physical Review Letters has published the results in its current issue as the Editors' Suggestion. This section highlights particularly interesting scientific results for the readers of the weekly journal, providing insight into fields outside the scope of their own research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Michael Förster
49-913-185-28874
Copyright © Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








