Home > Press > World's fastest quantum simulator operating at the atomic level
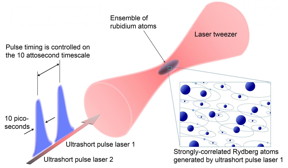 |
| Schematic explanation of the world's fastest quantum simulator. CREDIT NINS/IMS |
Abstract:
Kenji Ohmori (Institute for Molecular Science, National Institutes of Natural Sciences, Japan) has collaborated with Matthias Weidemüller (University of Heidelberg), Guido Pupillo (University of Strasbourg), Claudiu Genes (University of Innsbruck) and their coworkers to develop the world's fastest simulator that can simulate quantum mechanical dynamics of a large number of particles interacting with each other within one billionths of a second.
World's fastest quantum simulator operating at the atomic level
Okazaki, Japan | Posted on November 16th, 2016The dynamics of many electrons interacting with each other governs a variety of important physical and chemical phenomena such as superconductivity, magnetism, and chemical reactions. An ensemble of many particles thus interacting with each other is referred to as a "strongly correlated system". Understanding the properties of strongly correlated systems is thus one of the central goals of modern sciences. It is extremely difficult, however, to predict theoretically the properties of a strongly correlated system even if one uses the post-K supercomputer, which is one of the world's fastest supercomputers planned to be completed by the year 2020 in a national project of Japan. For example, the post-K cannot exactly calculate even the energy, which is the most basic property of matter, when the number of particles in the system is more than 30. Instead of calculating with a classical computer such as the post-K, an alternative concept has been proposed and referred to as a "quantum simulator", in which quantum mechanical particles such as atoms are assembled into an artificial strongly correlated system whose properties are known and controllable. The latter is then used to simulate and understand the properties of a different strongly correlated system, whose properties are not known. Huge investment to the development of quantum simulators has therefore been started recently in national projects of various countries including US, EU, and China.
The team has developed a completely new quantum simulator that can simulate the dynamics of a strongly correlated system of more than 40 atoms within one billionths of a second. This has been realized by introducing a novel approach in which an ultrashort laser pulse whose pulse-width is only 100 billionths of a second is employed to control a high-density ensemble of atoms cooled down to temperatures close to absolute zero. Furthermore they have succeeded in simulating the motion of electrons of this strongly correlated system that is modulated by changing the strength of interactions among many atoms in the ensemble.
This "ultrafast quantum simulator" is expected to serve as a basic tool to investigate the origin of physical properties of matter including magnetism and, possibly, superconductivity.
This result will be published in Nature Communications, an online scientific journal of UK, on 16th November 2016.
###
(Information of the paper)
Journal: Nature Communications
Title: Direct observation of ultrafast many-body electron dynamics in an ultracold Rydberg gas
Authors: Nobuyuki Takei, Christian Sommer, Claudiu Genes, Guido Pupillo, Haruka Goto, Kuniaki Koyasu, Hisashi Chiba, Matthias Weidemüller, and Kenji Ohmori
Date: 2016/11/16
DOI: 10.1038/NCOMMS13449
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kenji Ohmori
Professor and Chairman, Department of Photo-Molecular Science, Institute for Molecular Science, National Institutes of Natural Sciences
38 Nishigo-Naka, Myodaiji, Okazaki 444-8585, Japan
Tel?+81-564-55-7361?Fax?+81-564-54-2254
URL: https://groups.ims.ac.jp/organization/ohmori_g/index-e.html
(Press contact)
Public Relations, Institute for Molecular Science, Natural Institutes of Natural Sciences
TEL/FAX?+81-564-55-7262
Copyright © National Institutes of Natural Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








