Home > Press > The molecular mechanism that blocks membrane receptors has been identified: The work in which the Ikerbasque researcher of the Biofisika Institute Xabier Contreras has participated has been published in the journal Cell
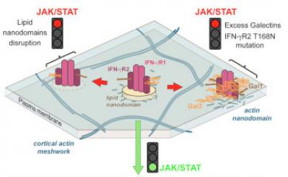 |
| The activation of the intracellular signalling of the IFN-gR receptor depends on the lipid nanodomains present in the membrane. The alteration of these nanodomains or the presence of a single mutation in the receptor induces galectin binding. The receptor ends up trapped in the actin filaments and cell signalling is blocked. CREDIT Instituto Biofisika (UPV/EHU, CSIC) |
Abstract:
The study began by taking the medical history of 11 children, all of whom had a disorder due to mycobacteria infections, as the basis. All were discovered to have the same phenotype with the same mutation, which was located in the interferon-gamma (IFNGR) receptor, so the group began to explore what was causing this dysfunction.
The molecular mechanism that blocks membrane receptors has been identified: The work in which the Ikerbasque researcher of the Biofisika Institute Xabier Contreras has participated has been published in the journal Cell
Leioa, Bizkaia | Posted on October 27th, 2016The cell membrane can be likened to an ocean, a sea consisting mainly of lipids and proteins, in which there are islands made up of specific lipids such as cholesterol and sphingolipids. The membrane proteins are located on the islands and can only perform their function in these nanodomains.
The IFNGR receptor is one of these membrane proteins and undertakes to activate genes involved in a huge variety of cell processes, including defence against pathogens and cancer. The team discovered that a simple mutation in the chain of 337 aminoacids that form it allows a sugar to be added. This sugar is recognised by a protein in the family of extracellular proteins known as galectins. When that protein is added to the receptor, the receptor gets taken out of its nanodomain and becomes caught up in the actin filaments that form the cell's cytoskeleton. Once outside its nanodomain, the receptor becomes blocked and can no longer transmit the signal.
"The research provides direct evidence on the fundamental role that certain lipid nanodomains play in the activation and regulation of cell signalling mediated by the IFNGR receptor. What is more, the results of this work stress the need to study the interaction between galectins and highly glycosylated membrane receptors and the link with various congenital diseases," pointed out Xabier Contreras. The study is also offering possible therapeutic targets for treating patients who are carriers of the IFNGR receptor mutation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matxalen Sotillo
34-688-673-770
Copyright © University of Basque Country
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








