Home > Press > Unraveling the crystal structure of a -70° Celsius superconductor, a world first: Significant advancement in the realization of room-temperature superconductors
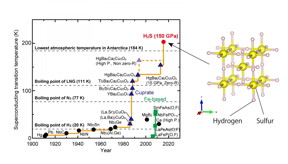 |
| (Left) Development of the superconducting transition temperature Tc. Hydrogen sulfide's highest Tc is H2S (150 GPa), and this is 30 K higher than what was previously the highest Tc superconductor � Cuprate, Hg-Ba2Ca2Cu3Oy -- and the lowest temperature ever recorded on the Earth's surface to date (184 K/-93�). CREDIT: Osaka University |
Abstract:
For the first time in the world, a research group led by Osaka University, Japan, clarified the crystal structure of hydrogen sulfide in its superconducting phase at the high temperature of -70°C. This was achieved by conducting a combination of experiments at one of the world's largest synchrotron radiation facilities, SPring-8 in Japan. These results mark a huge step towards developing room-temperature superconductors, which may provide promising solutions to energy problems.
Unraveling the crystal structure of a -70° Celsius superconductor, a world first: Significant advancement in the realization of room-temperature superconductors
Osaka, Japan | Posted on August 25th, 2016Superconductivity is a phenomenon that occurs when the electrical resistance of materials reaches zero as they are cooled down to a certain temperature. While the possible scenarios for its use are manifold, such as using superconductors as energy transmission lines without energy loss, widespread use is difficult as costs for cooling are high. Last year, hydrogen sulfide set a new record for highest superconducting transition temperature under high pressure. However, its crystal structure, necessary for understanding its superconductivity mechanism, was not understood. A research group led by Prof. Katsuya Shimizu and Dr. Mari Einaga at the Center for Science and Technology Under Extreme Conditions, Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University, together with Dr. Mikhail Eremets at the Max Planck Institute for Chemistry, and Dr. Yasuo Ohishi at the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute, has now succeeded in clarifying this structure by simultaneously conducting measurements of high pressure electrical resistance and X-ray diffraction.
Since hydrogen sulfide consists of light elements, measurements required a special setup. Therefore, these measurements were conducted at the synchrotron radiation facility SPring-8, and consisted of using a diamond anvil cell to conduct measurement under high-pressure and low temperature, and the high-pressure beam line BL10XU with which high-intensity, high-energy and micro-diameter X-ray beams for X-ray diffraction can be used, in order to examine the material's crystal structure. The researchers clarified that under high pressure, H2S molecules underwent a structural change to H3S and that this H3S structure exhibited superconductivity. Furthermore, from simultaneously measuring changes in pressure of superconducting transition temperature, they discovered that H3S displayed two superconducting phases: one with a cubic structure, the other with a hexagonal structure. They thereby managed to prove previous predictions from theoretical calculations.
The results of this study will contribute to clarifying the mechanisms of the high-temperature superconductivity observed in hydrogen sulfide. They also mark a considerable step in developing room-temperature superconductors and provide new insights that will be useful in the development of new materials that spread under high pressure.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mari Einaga
81-668-506-658
Copyright © Osaka University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








