Home > Press > ORNL optimizes formula for cadmium-tellurium solar cells
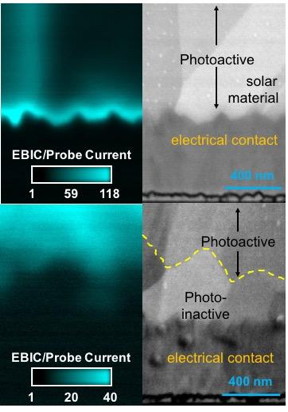 |
| The entire solar material for the sample with less than or equal to 30 percent selenium is photoactive (top) while the bottom of the solar material for the image below contains greater than 35 percent selenium and has reduced photoactivity. CREDIT: ORNL |
Abstract:
Solar cells based on cadmium and tellurium could move closer to theoretical levels of efficiency because of some sleuthing by researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
ORNL optimizes formula for cadmium-tellurium solar cells
Oak Ridge, TN | Posted on August 5th, 2016A team led by Jonathan Poplawsky of the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences used advanced microscopy techniques to discover efficiency differences of crystalline structures of various mixtures of cadmium, tellurium and selenium. In fact, selenium is an integral part of the formulation that resulted in a world record for solar cell efficiency. The team's paper is published in Nature Communications.
While some of today's solar cells use a blend of cadmium and tellurium to convert light into electricity, adding the optimum amount of selenium in the right places could help increase efficiency from the current mark of about 22 percent to levels approaching the theoretical limit of 30-33 percent. The trick is to determine the best ratio of selenium.
"Using different microscopy methods, we were able to gain a better understanding of the phases, compositions and crystalline structures that allow these materials to convert light into electricity more efficiently," said Poplawsky, adding that the availability of data is limited. "In some instances, adding too much selenium changes the crystalline structure of cadmium-tellurium and dramatically reduces the conversion efficiency."
For this study, researchers studied four solar cells with different selenium contents - and corresponding changes in crystal structure - and learned that the one with the highest level of selenium did not perform well. Neither did the one with the lowest selenium content. The alloy composition that performed best consisted of approximately 50 percent cadmium, 25 percent tellurium and 25 percent selenium.
To make their determination, researchers used a combination of analytical techniques, including atom probe tomography, transmission electron microscopy and electron beam induced current. These are capabilities within the CNMS, a DOE Office of Science User Facility.
"We have shown that the amount of selenium incorporated into the cadmium-tellurium controls whether the small crystals inside the solar cell form as crystal structure A or crystal structure B," Poplawsky said. "This information can be used as a roadmap for solar cell producers to make improved cadmium-tellurium solar cells that use selenium additions, and hopefully increase the overall efficiency."
Poplawsky noted that solar panels typically use silicon as the material for converting sunlight into electricity. Cadmium-telluride, however, has an advantage over silicon because it can absorb the same amount of sunlight with 98 percent less semiconducting material, thus reducing the overall cost of the solar panel. This also makes solar panels composed of cadmium, tellurium and selenium more competitive with other forms of electricity generation.
###
ORNL co-authors of the paper, titled "Structure and Compositional Dependence on the CdTexSe1-x Alloy Layer Photoactivity in CdTe-based Solar Cells," are Wei Guo, Karren More and Donovan Leonard.
This research was funded by DOE's SunShot Initiative in collaboration with the National Sciences Foundation.
####
About Oak Ridge National Laboratory
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for the DOE's Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov/.
About the SunShot Initiative
The SunShot Initiative is a collaborative national effort that aggressively drives innovation to make solar energy fully cost-competitive with traditional energy sources before the end of the decade. Through SunShot, the Energy Department supports efforts by private companies, universities, and national laboratories to drive down the cost of solar electricity to $0.06 per kilowatt-hour. Learn more at energy.gov/sunshot.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ron Walli
865-576-0226
Copyright © Oak Ridge National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








