Home > Press > Novel state of matter: Observation of a quantum spin liquid
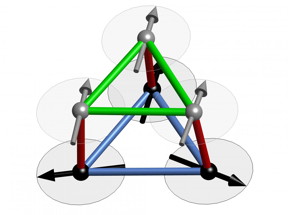 |
| This is a section from the crystal lattice of Calcium-chromium oxide showing how the spins are subject to conflicting demands. In this ball-and-stick model, the green and red sticks connecting the atoms (grey and black balls) represent ferromagnetic interactions while the blue sticks represent anti-ferromagnetic interactions. CREDIT: HZB |
Abstract:
Based on our everyday experience, we expect matter at low temperatures to freeze solid with the atoms fixed in a regular arrangement. The magnetic moments arising from the spins of the electrons on the atoms in magnetic materials, also come to rest and become rigidly oriented as temperature falls. However, there are some rare exceptions. In what are referred to as quantum spin liquids, the orientations of the electronic spins do not remain fixed even at temperatures near absolute zero. According to conventional understanding, if the interactions are isotropic (where all spin directions are possible), this phenomenon can occur if the spins are arranged in triangular geometries and the interactions between them are antiferromagnetic favouring antiparallel alignment of the spins. For three atoms forming the corners of a triangle, the electronic spin of one atom cannot simultaneously be oriented antiparallel to those on both the other two atoms. In real materials that contain triangular units coupled by antiferromagnetic interactions this "frustration" can prevent the spins from coming to rest in a particular orientation even at absolute zero temperature, instead they move collectively like atoms in a liquid. By contrast, ferromagnetic interactions do not give rise to frustration in isotropic magnets because mutually parallel alignment of the spins can always occur. For these reasons, only a few isotropic materials have been proposed as spin liquid candidates.
Novel state of matter: Observation of a quantum spin liquid
Berlin, Germany | Posted on July 29th, 2016Monocrystals with complex magnetic interactions
Now a team headed by Prof. Bella Lake has produced and investigated the first monocrystals of calcium-chromium oxide (Ca10Cr7O28). Calcium-chromium oxide is made up of what are known as Kagomé lattices - reminiscent of the pattern of triangles and hexagons woven in Japanese basketry. As a result, a complex set of isotropic magnetic interactions develop in this material, consisting of not only anti-ferromagnetic interactions but also much stronger ferromagnetic interactions that according to conventional understanding should prevent the existence of spin liquid behavior. Magnetic and Neutron scattering experiments conducted in Germany, France, England, and the USA, as well as muon spectroscopy experiments performed in Switzerland have however shown that the spins in these samples retain their collective motion even at temperatures as low as 20 millikelvin and behave like a quantum spin liquid.
Competition is key
Theoretical physicist Prof. Johannes Reuther of HZB has now been able to extend the theoretical model of spin liquids with the help of these experimental clues. He has used numerical simulations to show how the different magnetic interactions in calcium-chromium oxide compete with one another and keep the spins dynamic.
More candidates für spin liquids expected
"We have proved empirically that interesting quantum states like spin liquids can also occur in considerably more complex crystals with different constellations of magnetic interactions", says Dr. Christian Balz, lead author of the work. Lake also explains: "The work expands our understanding of magnetic materials, and also shows us that there are potentially far more candidates for spin liquids than expected. This could be important for the advancement of quantum computers in the future because spin liquids are one of the possible building blocks for carrying the smallest unit of quantum information, known as a qubit."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Antonia Roetger
49-308-062-43733
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie (HZB)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








