Home > Press > Scientists move closer to developing therapeutic window to the brain: Transparent skull implant created by UCR-led team will allow doctors to deliver life-saving laser treatments to patients with brain disorders
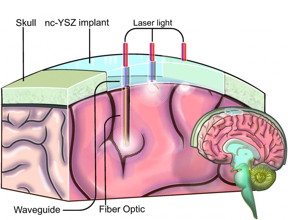 |
| This is an illustration showing how the "Window to the Brain" transparent skull implant created by UC Riverside researchers would work. CREDIT: UC Riverside |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of California, Riverside are bringing their idea for a 'Window to the Brain' transparent skull implant closer to reality through the findings of two studies that are forthcoming in the journals Lasers in Surgery and Medicine and Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine.
Scientists move closer to developing therapeutic window to the brain: Transparent skull implant created by UCR-led team will allow doctors to deliver life-saving laser treatments to patients with brain disorders
Riverside, CA | Posted on July 13th, 2016The implant under development, which literally provides a 'window to the brain,' will allow doctors to deliver minimally invasive, laser-based treatments to patients with life-threatening neurological disorders, such as brain cancers, traumatic brain injuries, neurodegenerative diseases and stroke. The recent studies highlight both the biocompatibility of the implant material and its ability to endure bacterial infections.
The Window to the Brain project is a multi-institution, interdisciplinary partnership led by Guillermo Aguilar, professor of mechanical engineering in UCR's Bourns College of Engineering, and Santiago Camacho-López, from the Centro de Investigación Científica y de Educación Superior de Ensenada (CICESE) in Mexico.
The project began when Aguilar and his team developed a transparent version of the material yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ)--the same ceramic product used in hip implants and dental crowns. By using this as a window-like implant, the team hopes doctors will be able to aim laser-based treatments into patients' brains on demand and without having to perform repeated craniotomies, which are highly invasive procedures used to access the brain.
The internal toughness of YSZ, which is more impact resistant than glass-based materials developed by other researchers, also makes it the only transparent skull implant that could conceivably be used in humans. The two recent studies further support YSZ as a promising alternative for currently available cranial implants.
Published July 8 in Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, the most recent study demonstrates how the use of transparent YSZ may allow doctors to combat bacterial infections, which are a leading reason for cranial implant failure. In lab studies, the researchers treated E-Coli infections by aiming laser light through the implant without having to remove it and without damaging the surrounding tissues.
"This was an important finding because it showed that the combination of our transparent implant and laser-based therapies enables us to treat not only brain disorders, but also to tackle bacterial infections that are common after cranial implants. These infections are especially challenging to treat because many antibiotics do not penetrate the blood brain barrier," said Devin Binder, M.D., a neurosurgeon and neuroscientist in UCR's School of Medicine and a collaborator on the project.
Another recent study, published in the journal Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, explored the biocompatibility of YSZ in an animal model, where it integrated into the host tissue without causing an immune response or other adverse effects.
"The YSZ was actually found to be more biocompatible than currently available materials, such as titanium or thermo-plastic polymers, so this was another piece of good news in our development of transparent YSZ as the material of choice for cranial implants," Aguilar said.
The Window to the Brain team comprises faculty at UCR's Bourns College of Engineering and School of Medicine together with researchers at the University of California, San Diego and three universities in Mexico: Centro de Investigación Científica y de Educación Superior de Ensenada (CICESE); Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM); and Rubén Ramos-García, Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica, Óptica y Electrónica (INAOE) in Puebla. Yasaman Damestani, a graduate student in Aguilar's lab, was the lead author of these recent research studies.
Last October, the team received almost $5 million to advance the project over five years. $3.6 million was from the National Science Foundation's Partnerships in International Research and Education (PIRE) program, which pairs U.S. universities with others around the world. An additional $1 million was from Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT), Mexico's entity in charge of promoting scientific and technological activities. The remainder of the money came from in-kind contributions from the Mexican universities.
The team's long-term goal is to see the technology become the standard of care for patients with brain disorders who would benefit from laser-based treatments.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah Nightingale
951-827-4580
Copyright © University of California - Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Brain-Computer Interfaces
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
![]() New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








