Home > Press > A drop of water as a model for the interplay of adhesion and stiction
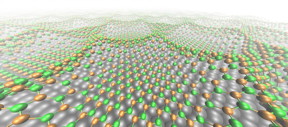 |
| The boron nitride nanomesh superhoneycomb: nitrogen (green), boron (orange), rhodium (grey); distance between honeycombs 3.2 nm. CREDIT: Marcella Iannuzzi, UZH & Ari Seitsonen, ENS Paris |
Abstract:
How can a gecko move across a ceiling upside down? Two mechanisms are responsible: Adhesion via billions of extremely fine hairs on its feet, which enable it to stick to ceilings and walls. And as soon as the gecko moves, it relies on stiction. However, any change of adhesion and stiction at macroscopic level is expressed on the nanometer scale through the change in the forces exerted between atoms and molecules.
A drop of water as a model for the interplay of adhesion and stiction
Zurich, Switzerland | Posted on June 30th, 2016How a drop of water touches a honeycomb structure
An international team of researchers headed by Thomas Greber from the University of Zurich's Physik-Institut succeeded in changing the manner in which a drop of liquid adheres to a surface by altering the electric voltage applied to a water drop. The surface upon which the drop lies consists of a material known as nanomesh, a single boron nitride layer on metallic rhodium. The structure is shaped like honeycomb with a comb depth of 0.1 nanometers and comb-comb distance of 3.2 nanometers.
Macroscopically, the change in electrical voltage is expressed in the change of the contact angle between the drop and the nanomesh surface. The contact or wetting angle refers to the angle that a drop of liquid assumes with respect to the surface of a solid. This angle can be measured with the aid of backlit photographs.
Change in the surface structure alters the contact angle of the drop
On the nanometer scale, the change in voltage causes the following: The nitrogen bonds with the rhodium are replaced by hydrogen-rhodium bonds, which flattens the nanomesh structure. How strongly the boron nitride's nitrogen binds to the surface of the rhodium depends on its distance from and direction to the next rhodium atom. And this determines the honeycomb structure and depth of the boron nitride layer. If the voltage changes, hydrogen accumulates between the boron nitride and the rhodium layer, which causes the honeycomb boron nitride layer to become flat. Tunneling microscopy can be used to detect this nanoscopic effect - the change in the surface properties of the nanomesh - in the liquid.
"To understand and control the interplay between the macro and the nano-world is the real challenge in nanoscience," stresses Greber. After all, six orders of magnitude need to be bridged - from millimeters in length (10-3 m) to nanometers (10-9 m); that's a factor of one million. "Our model system of the electrically switchable nanomesh and a drop's observable contact angle enables us to access the fundamental phenomenon of the friction of liquids on surfaces more precisely. This should help us solve problems that crop up during lubrication more effectively, for instance." The research project actually appears on the cover of the latest issue of the renowned journal Nature.
On the one hand, the new system is interesting for biology. Applying this effect should make it possible to control the adhesion and movement of cells. Aspects such as cell migration or the formation of complex, multicellular structures with new scientific approaches might be researched as a result. On the other hand, technological applications such as capillary pumps, where the capillary height can be controlled via electrical voltage, or micro-capillaries, where the flow resistance can be controlled, are also conceivable.
###
About the study
The research results were achieved within the scope of the Sinergia Program of the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF). The SNSF uses this instrument to promote the collaboration between several research groups, which conduct research across disciplines with the prospect of ground-breaking results. Besides the University of Zurich, the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Vienna University of Technology and Empa were also involved.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Thomas Greber
41-446-355-744
Copyright © University of Zurich
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








