Home > Press > Drug candidate shrinks tumor when delivered by plant virus nanoparticle: Phenanthriplatin outperformed cisplatin in mouse model of triple-negative breast cancer when encapsulated into nanocarrier
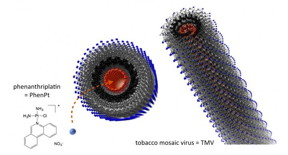 |
| When packaged inside tobacco mosaic virus nanoparticles, phenanthriplatin is delivered to tumors, where it was shown to be more effective in vivo than an approved platin. CREDIT: Case Western Reserve University |
Abstract:
In a pair of firsts, researchers at Case Western Reserve University and Massachusetts Institute of Technology have shown that the drug candidate phenanthriplatin can be more effective than an approved drug in vivo, and that a plant-virus-based carrier successfully delivers a drug in vivo.
Drug candidate shrinks tumor when delivered by plant virus nanoparticle: Phenanthriplatin outperformed cisplatin in mouse model of triple-negative breast cancer when encapsulated into nanocarrier
Cleveland, OH | Posted on June 10th, 2016Triple-negative breast cancer tumors of mice treated with the phenanthriplatin -carrying nanoparticles were four times smaller than those treated either with cisplatin, a common and related chemotherapy drug, or free phenanthriplatin injected intravenously into circulation.
The scientists believe the work, reported in the journal ACS Nano, is a promising step toward clinical trials.
"We may have found the perfect carrier for this particular drug candidate," said Nicole Steinmetz, an assistant professor of biomedical engineering at Case Western Reserve, who has spent 10 years studying the use of plant viruses for medical purposes.
She teamed with Stephen J. Lippard, Arthur Amos Noyes Professor of chemistry at MIT, and an expert in biological interactions involving platinum-based chemotherapies.
Platinum-based drugs are used to treat more than half of cancer patients receiving chemotherapy. Two of the most commonly used drugs are cisplatin and carboplatin. They form bifunctional cross-links with DNA in cancer cells, which block the DNA from transcribing genes and result in cell death, Lippard explained.
Despite widespread use, cisplatin has been shown to cure only testicular cancer, and many cancers have or develop immunity to the drug.
Lippard's lab altered cisplatin by replacing a chloride ion with phenanthridine and found that the new molecule also binds to DNA. Instead of forming cross-links, however, phenanthriplatin binds to a single site but still blocks transcription.
In fact, his lab found that phenanthriplatin is up to 40 times more potent than traditional platins when tested directly against cancer cells of lung, breast, bone and other tissues. The molecule also appears to avoid defense mechanisms that convey resistance.
But when injected into mouse models of cancer, the drug candidate performed no better than standard platins.
Lippard realized phenanthriplatin wasn't reaching its target. He had a drug delivery problem.
He found a potential solution while visiting Case Western Reserve's campus and heard Steinmetz explain her work investigating tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) for drug delivery more than a year ago.
"I envisioned that TMV would be the perfect vehicle," Lippard said. "So we had a beer and formed a collaboration."
The long, thin tobacco mosaic virus nanoparticles are naturals for delivering the drug candidate into tumors, said Steinmetz, who was appointed by the Case Western Reserve School of Medicine.
The virus particles, which won't infect humans, are hollow. A central tube about 4 nanometers in diameter runs the length of the shell and the lining carries a negative charge.
Phenanthriplatin is about 1 nanometer across and, when treated with silver nitrate, has a strong positive charge. It readily enters and binds to the central lining.
The elongated shape of the nanoparticle causes it to tumble along the margins of blood vessels, remain unnoticed by immune cells and pass through the leaky vasculature of tumors and accumulate inside. Little healthy tissue is exposed to the toxic drug.
Inside tumors, the nanoparticles gather inside the lysosomal compartments of cancer cells, where they are, in essence, digested. The pH is much lower than in the circulating blood, Steinmetz explained. The shell deteriorates and releases phenanthriplatin.
The shell is broken down into proteins and cleared through metabolic or natural cellular processes within a day while the drug candidate starts blocking transcription, leading to greater amounts of cell death through apoptosis than cross-linking platins.
The researchers say delivery of the phenanthriplatin into the tumor led to its improved performance over cisplatin or free phenanthriplatin.
Lippard and Steinmetz continue to collaborate, investigating use of this system to deliver other drugs or drug candidates, use in other types of cancers, the addition of agents on the exterior of the shell to increase accumulation inside tumors and more.
###
Other authors of the paper are Anna E. Czapar, PhD student in pathology at the Case Western Reserve School of Medicine; and Sourabh Shukla, research assistant professor in biomedical engineering at Case Western Reserve; and MIT's Yao-Rong Zheng, Imogen Riddell and Samuel G. Awuah, postdoctoral researchers in Lippard's lab.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kevin Mayhood
216-534-7183
Copyright © Case Western Reserve University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








