Home > Press > Microwaved nanoribbons may bolster oil and gas wells: Rice University researchers microwave a composite to toughen wellbore walls
 |
| http://news.rice.edu/files/2016/05/0516_WELL-1-GRAPHIC-WEB-1gzfk5y.jpg
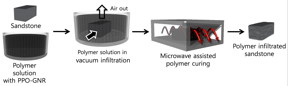
Rice University researchers have developed a method to treat composite materials of graphene nanoribbons and thermoset polymers with microwaves in a way that could dramatically reinforce wellbores for oil and gas production. Credit: Nam Dong Kim/Rice University |
Abstract:
Wellbores drilled to extract oil and gas can be dramatically reinforced with a small amount of modified graphene nanoribbons added to a polymer and microwaved, according to Rice University researchers.
Microwaved nanoribbons may bolster oil and gas wells: Rice University researchers microwave a composite to toughen wellbore walls
Houston, TX | Posted on May 12th, 2016The Rice labs of chemist James Tour and civil and environmental engineer Rouzbeh Shahsavari combined the nanoribbons with an oil-based thermoset polymer intended to make wells more stable and cut production costs. When cured in place with low-power microwaves emanating from the drill assembly, the composite would plug the microscopic fractures that allow drilling fluid to seep through and destabilize the walls.
Results of their study appeared in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces.
The researchers said that in the past, drillers have tried to plug fractures with mica, calcium carbonate, gilsonite and asphalt to little avail because the particles are too large and the method is not efficient enough to stabilize the wellbore.
In lab tests, a polymer-nanoribbon mixture was placed on a sandstone block, similar to the rock that is encountered in many wells. The team found that rapidly heating the graphene nanoribbons to more than 200 degrees Celsius with a 30-watt microwave was enough to cause crosslinking in the polymer that had infiltrated the sandstone, Tour said. The microwave energy needed is just a fraction of that typically used by a kitchen appliance, he said.
"This is a far more practical and cost-effective way to increase the stability of a well over a long period," Tour said.
In the lab, the nanoribbons were functionalized -- or modified -- with polypropylene oxide to aid their dispersal in the polymer.
Mechanical tests on composite-reinforced sandstone showed the process increased its average strength from 5.8 to 13.3 megapascals, a 130 percent boost in this measurement of internal pressure, Shahsavari said. Similarly, the toughness of the composite increased by a factor of six.
"That indicates the composite can absorb about six times more energy before failure," he said.
"Mechanical testing at smaller scales via nanoindentation exhibited even more local enhancement, mainly due to the strong interaction between nanoribbons and the polymer. This, combined with the filling effect of the nanoribbon-polymer into the pore spaces of the sandstone, led to the observed enhancements."
The researchers suggested a low-power microwave attachment on the drill head would allow for in-well curing of the nanoribbon-polymer solution.
Lead authors of the paper are postdoctoral researcher Nam Dong Kim and graduate student Andrew Metzger, both of Rice. Co-authors are postdoctoral researchers Vahid Hejazi and Seoung-Ki Lee, graduate students Yilun Li and Ruquan Ye, alumni Jason Mann and Anton Kovalchuk and research scientist Carter Kittrell, all of Rice. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering. Shahsavari is an assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering and of materials science and nanoengineering.
MI-SWACO, a Schlumberger company, partially supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Multiscale Materials Laboratory (Shahsavari):
Multiscale Materials Laboratory (Shahsavari):
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Mining/Extraction/Drilling
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








