Home > Press > Clay nanotube-biopolymer composite scaffolds for tissue engineering
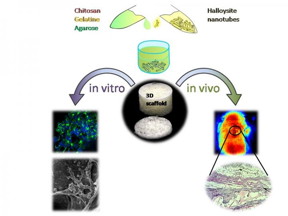 |
| A sketch demonstrating the fabrication and in vitro and in vivo testing of novel halloysite-doped biopolymer tissue engineering scaffold CREDIT: Bionanotechnology Lab, Institute of Fundamental Medicine and Biology, Kazan Federal University, |
Abstract:
The fabrication of a prototype tissue having functional properties close to the natural ones is crucial for effective transplantation. Tissue engineering scaffolds are typically used as supports which allow cells to form tissue-like structures essentially required for the correct functioning of the cells under the conditions close to the three-dimensional tissue.
Clay nanotube-biopolymer composite scaffolds for tissue engineering
Kazan, Russia Federation | Posted on May 1st, 2016Scientists of Bionanotechnology Lab, Kazan Federal University, combined three biopolymers, chitosan and agarose (polysaccharides), and a protein gelatine, as the materials to produce tissue engineering scaffolds and demonstrated the enhancement of mechanical strength (doubled pick load), higher water uptake and thermal properties in chitosan-gelatine-agarose hydrogels doped with halloysite.
Chitosan, a natural biodegradable and chemically versatile biopolymer, has been effectively used in antibacterial, antifungal, anti-tumour and immunostimulating formulations. To overcome the disadvantages of pure chitosan scaffolds such as mechanical fragility and low biological resistance, chitosan scaffolds are typically doped with other supporting compounds which allow for mechanical strengthening, thus yielding ?omposite biologically resistant scaffolds.
Agarose is a galactose-based backbone polysaccharide isolated from red algae, having remarkable mechanical properties which are useful in the design of tissue engineering scaffolds.
Gelatine is formed from collagen by hydrolysis (breaking the triple-helix structure into single-strand molecules) and has a number of advantages over its precursor. It is less immunogenic compared with collagen and it retains informational signal sequences promoting cell adhesion, migration, differentiation and proliferation.
The surface irregularities of the scaffold pores due to the insoluble nanosized components promote the best adhesion of the cells on scaffold materials, while the nanoparticle fillers increase the composites' strength. Thus, researchers doped halloysite nanotubes into a chitosan-agarose-gelatine matrix to design the implantable 3D cell scaffolds.
The resulting scaffolds demonstrate the shape memory upon deformation and have the porous structure suitable for cell adhesion and proliferation which is essential for artificial tissue fabrication. Macroscopic observations have confirmed that all the samples of scaffolds exhibited the sponge-like behaviour with the shape memory and shape reconstitution after deformation both in wet and dry states.
The swelling experiments indicated that the addition of halloysite can greatly improve the hydrophilicity and wetting of composite scaffolds. The incorporation of halloysite nanotubes into the scaffolds increases the water uptake and subsequently improves the biocompatibility. The intrinsic properties of halloysite nanotubes can be used for further improving the biocompatibility of scaffolds by the loading and sustained release of different bioactive compounds. This opens the prospect for fabrication of scaffolds with defined properties for directed differentiation of cells on matrixes due to gradual release of differentiation factors.
Experiments on two types of human cancer cells (A549 and Hep3B) show that in vitro cell adhesion and proliferation on the nanocomposites occur without changes in viability and cytoskeleton formation.
Further in vivo biocompatibility and biodegradability evaluation in rats has confirmed that the scaffolds promote the formation of novel blood vessels around the implantation sites. The scaffolds show excellent resorption within six weeks after implantation in rats. Neo-vascularization observed in newly formed connective tissue placed near the scaffold allows for the complete restoration of blood flow.
The results obtained indicate that the halloysite doped scaffolds are biocompatible as demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo. In addition, they confirm the great potential of chitosan-agarose-gelatine nanocomposite porous scaffolds doped with halloysite in tissue engineering with potential for sustained nanotube drug delivery.
###
The work is performed according to the Russian Government Program of Competitive Growth of Kazan Federal University.
This work was funded by the subsidy allocated to Kazan
Federal University for the state assignment in the sphere of scientific activities. The authors acknowledge the support by the RFBR grant 15-34-20583 mol_a_ved.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yevgeniya Litvinova
7-843-233-7345
Copyright © Kazan Federal University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








