Home > Press > Physicists detect the enigmatic spin momentum of light
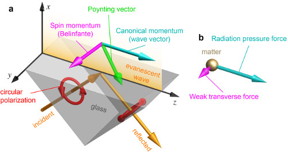 |
| Canonical and spin momenta of light in an evanescent wave
a, The figure shows an evanescent wave generated by the total internal reflection of a polarized plane wave at a glass–air interface. It carries longitudinal canonical momentum determined by its wavevector and exhibits transverse spin momentum determined by the degree of circular polarization of the field. b, The longitudinal canonical momentum produces the well-known radiation pressure in light–matter interactions, whereas the transverse spin momentum exerts a weak helicity-dependent force orthogonal to the propagation direction of light. Credit: RIKEN |
Abstract:
Ever since Kepler's observation in the 17th century that sunlight is one of the reasons that the tails of comets to always face away from the sun, it has been understood that light exerts pressure in the direction it propagates. Radiation pressure is produced by the momentum carried by light, and it plays a crucial role in a variety of systems, from atomic to astronomical scales.
Physicists detect the enigmatic spin momentum of light
Wako, Japan | Posted on April 26th, 2016In a recent theoretical paper (Extraordinary momentum and spin in evanescent waves Konstantin Y. Bliokh, Aleksandr Y. Bekshaev, Franco Nori Nature Communications, 2014 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4300), a group from the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science in Japan showed that momentum density in non-uniform optical fields has an unusual component, which is orthogonal to the propagation direction of light and is proportional to the optical spin, which means the degree of circular polarization. They predicted that this spin momentum would produce a transverse spin-dependent optical force, a few orders of magnitude weaker than the usual radiation pressure.
Now, based on the theoretical work, a group from RIKEN, the University of Bristol, and other institutions have used an extremely precise technique to experimentally verify that light does in fact exert the extraordinary perpendicular force, which is determined by the polarization of the light. The research has been published in Nature Physics.
To measure the new type of optical momentum and force, they used an extremely sensitive nano-cantilever, capable of femtoNewton resolution--meaning it could measure a force even smaller than the force gravity exerts on a single bacterium--which was immersed in an evanescent optical field directly above a total-internal-reflecting glass surface.
According to Konstantin Bliokh, the corresponding author of the paper, "Our findings revisit fundamental momentum properties of light and, revealing a new type of optical force, enrich optomechanics."
Looking to the future, Franco Nori, who led the research team, says, "Our group's investigations integrate relativistic field-theoretical, quantum-mechanical, and optical aspects of the dynamical properties of light. They offer a new paradigm which could provide insights into a variety of phenomena: from applied optics to high-energy physics."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jens Wilkinson
RIKEN Global Relations and Research Coordination Office
Tel: +81-(0)48-462-1225 / Fax: +81-(0)48-463-3687
Copyright © RIKEN
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








