Home > Press > Quantum simulation 2.0: Atoms chat long distance: Physicists have measured long-range magnetic interactions between ultracold particles
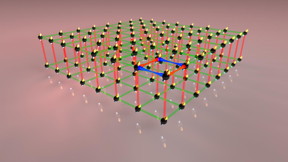 |
| By using a magnetic field physicists are able to directly change the direction of the mini magnets and precisely control how the particles interact. CREDIT: Erbium team/Simon Baier |
Abstract:
Simulations are a popular tool to study physical processes that cannot be investigated experimentally in detail. For example, scientists are challenged to investigate physical processes in materials since their properties are determined by the interactions of single particles, which are hardly measurable directly. Conventional computers quickly reach their limits when dealing with these complex simulations. At the beginning of the 1980s, Richard Feynman proposed to simulate these processes in a quantum system to overcome this obstacle. Two decades later, Ignacio Cirac and Peter Zoller presented concrete concepts of how quantum processes could be studied by using ultracold atoms confined in optical lattices. In the last few years, this approach has proven itself in practice and is now broadly applied in experiments. "We are able to control ultracold particles well in experiments and this has provided us with new insights into physical properties," says Francesca Ferlaino from the Institute for Experimental Physics of the University of Innsbruck and the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information of the Austrian Academy of Sciences. In collaboration with Peter Zoller's team of theoretical physicists, her research team has now extended this approach for quantum simulations and laid the groundwork for future new research: For the first time, the physicists were able to quantitatively measure long-range interactions between magnetic atoms in optical lattices.
Quantum simulation 2.0: Atoms chat long distance: Physicists have measured long-range magnetic interactions between ultracold particles
Innsbruck, Austria | Posted on April 11th, 2016Experimental tool box for matter
Many studies have focused on the investigation of the interaction of short-range particles. "In contrast, we are working with strongly magnetic atoms, which can also interact over long distances," says co-author Manfred Mark. For their experiment the physicists prepared an ultracold gas of erbium atoms - a Bose-Einstein condensate - in a three dimensional optical lattice of laser beams. In this simulated solid-body crystal, the particles were arranged similar to eggs in a carton. The distance between the particles was seven times their wave function in the Innsbruck experiment. "By using a magnetic field we are able to directly change the direction of the mini magnets and precisely control how the particles interact - attracting or repelling each other," explains first author Simon Baier.
A search for exotic quantum phases
"Our collaboration with Zoller, Cai Zi and Mikhail Baranov was indispensable for understanding our measurement results comprehensively," underlines Francesca Ferlaino. "Our work is another important step towards a better understanding of quantum matter of dipolar atoms because their nature is a lot more complex than the atoms used for ultracold quantum gases in other experiments." The research results also lay the groundwork for future studies of novel exotic many-body quantum phases such as checkerboard and stripe phases, which may be created by long-range interactions. "Our study opens the door to finally being able to measure these type of phases," says Simon Baier, who is already looking into the future. "In principle, we should be able to do this in our experiments as well but we will need to cool the atoms even further from currently 70nK to approximately 2nK."
###
The research is supported by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) and the European Research Council (ERC) among others.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Francesca Ferlaino
43-676-872-552-440
Copyright © University of Innsbruck
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








