Home > Press > Intracellular recordings using nanotower electrodes: Nanoscale-tipped high-aspect-ratio vertical microneedle electrodes for intracellular recordings
 |
Abstract:
Our current understanding of how the brain works is very poor. The electrical signals travel around the brain and throughout the body, and the electrical properties of the biological tissues are studied using electrophysiology. For acquiring a large amplitude and a high quality of neuronal signals, intracellular recording is a powerful methodology compared to extracellular recording to measure the voltage or current across the cell membranes. Nanowire- and nanotube-based devices have been developed for the intracellular recording applications to demonstrate the advantages of these devices having high spatial resolution and high sensitivity.
Intracellular recordings using nanotower electrodes: Nanoscale-tipped high-aspect-ratio vertical microneedle electrodes for intracellular recordings
Toyohashi, Japan | Posted on April 10th, 2016However, length of these nanowire/nanotube electrode devices is currently limited to less than 10 µm due to process issues that occur during fabrication of high-aspect-ratio nanoscale devices, which are more than 10-µm long. Thus, conventional nanodevices are not applicable to neurons/cells within thick biological tissues, including brain slices and brain in vivo.
A research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering and the Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary Research Institute (EIIRIS) at Toyohashi University of Technology has developed three-dimensional microneed?e-based nanoscale-tipped electrodes (NTEs) that are longer than 100 µm. The needle length exceeds that of the conventional nanowire/nanotube-based intracellular devices, thus expanding the range of applications of nanodevices in intracellular recording, such as deep tissue penetration. Additionally, they perform intracellular recordings using muscle cells.
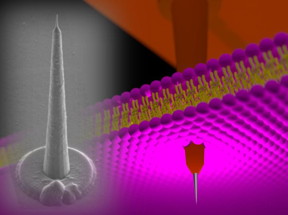
"A technological challenge in electrophysiology is intracellular recordings within a thick biological tissue. For example, a needle length of more than 40 µm is necessary for performing brain slice experiments. However, it is almost impossible to penetrate nanoscale diameter needles with a high-aspect-ratio, because of the long hair-like nanostructure that has insufficient stiffness. On the other hand, our NTE, which is 120-µm-long cone-shaped electrode, has sufficient stiffness to punch tissues and cells", explains the first author PhD candidate, Yoshihiro Kubota.
The leader of the research team, Associate Professor Takeshi Kawano said "Although we demonstrated the preliminary results of our NTE device, the batch fabrication of such intracellular electrodes, which have a needle length more than 100 µm, should lead to an advancement in the device technologies. This will eventually lead to realization of multisite, depth-intracellular recordings for biological tissues, including brain slices and brain in vivo, which are beyond the capability of conventional intracellular devices."
As addressed by the research team, the NTE has the potential to be used in cells that are deep within a biological tissue, including brain slice and brain in vivo, thus accelerating the understanding of the brain.
###
Funding agency:
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (S) (No. 20226010), (A) (No. 25249047), for Young Scientist (A) (No. 26709024), (B) (No. 22760251), and the PRESTO Program from JST. Yoshihiro Kubota was supported by the Leading Graduate School Program R03 of MEXT. Rika Numano was also supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (No. 24590350), the Asahi Glass Foundation and the Takeda Science Foundation.
####
About Toyohashi University of Technology
120-µm-height 'nanotower' electrode is punching a cell membrane. Silicon growth technology and three-dimensional nano/microfabrication techniques realize such high-aspect-ratio intracellular electrodes.
COPYRIGHT (C) TOYOHASHI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Contacts:
Ryoji Inada
Copyright © Toyohashi University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








