Home > Press > A movie of the microworld: Physicists create nanoparticle picture series
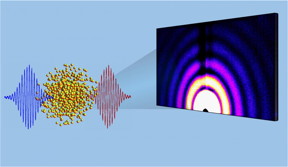 |
| Kansas State University physicists collaboratively have developed a method for taking X-ray images that show the explosion of superheated nanoparticles at the femtosecond level. CREDIT: Kansas State University |
Abstract:
Think of it as a microscopic movie: A sequence of X-ray images shows the explosion of superheated nanoparticles. The picture series reveals how the atoms in these particles move, how they form plasma and how the particles change shape.
A movie of the microworld: Physicists create nanoparticle picture series
Manhattan, KS | Posted on April 6th, 2016The method of taking these pictures is a collaborative creation that involved Kansas State University researchers Artem Rudenko and Daniel Rolles, both assistant professors of physics.
The movies help scientists understand interactions of intense laser light with matter. But even more importantly, these experiments lead the way to filming various processes that involve ultrafast dynamics of microscopic samples, such as the formation of aerosols -- which play a major role in climate models -- or laser-driven fusion.
"We can create a real movie of the microworld," Rudenko said. "The key development is that now we can take sequences of pictures on the nanoscale."
Rudenko and Rolles -- both affiliated with the university's James R. Macdonald Laboratory -- collaborated with researchers at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory at Stanford University, Argonne National Laboratory and the Max Planck Institutes in Germany. Their publication, "Femtosecond and nanometre visualization of structural dynamics in superheated nanoparticles," appears in Nature Photonics.
In this work, the collaboration used intense lasers to heat xenon nanoscale clusters and then took a series of X-ray pictures to show what happened to the particles. The picture series became a movie of how these objects move at the level of femtoseconds, which are one-millionth of a billionth of a second.
"What makes nano so interesting is that the behavior for many things changes when you get to the nanoscale," Rolles said. "Nano-objects bridge the gap between bulk matter and individual atoms or molecules. This research helps us as we try to understand the behavior of nano-objects and how they change shape and properties within extremely short times."
The pictures of the nanoparticles cannot be taken with normal optical light, but must be taken with X-rays because X-ray light has nanometer wavelengths that enable researchers to view nanoscale objects, Rolles said. The light wavelength must match the size of the object.
To take the pictures, the researchers needed two ingredients: very short X-ray pulses and very powerful X-ray pulses. The Linac Coherent Light Source at SLAC provided those two ingredients, and Rudenko and Rolles traveled to California to use this machine to take the perfect pictures.
The photo-taking method and the pictures it produces have numerous applications in physics and chemistry, Rolles said. The method is also valuable for visualizing laser interactions with nanoparticles and for the rapidly developing field of nanoplasmonics, in which the properties of nanoparticles are manipulated with intense light fields. This may help to build next-generation electronics.
"Light-driven electronics can be much faster than conventional electronics because the key processes will be driven by light, which can be extremely fast," Rudenko said. "This research has big potential for optoelectronics, but in order to improve technology, we need to know how a laser drives those nanoparticles. The movie-making technology is an important step in this direction."
Rudenko and Rolles are continuing to improve the moviemaking process. In collaboration with the university's soft matter physics group, they have extended the range of samples, which can be put into the X-ray machine and now can produce movies of gold and silica nanoparticles.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jennifer Tidball
785-532-0847
Copyright © Kansas State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








