Home > Press > Nanoparticle-based cancer therapies shown to work in humans
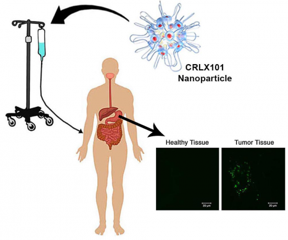 |
| The nanoparticle therapeutic CRLX101 (schematic illustration provided by Cerulean Pharma Inc.) was given intravenously to patients with stomach cancer. Biopsies were taken of both the stomach tumor and nearby, healthy tissue. Evidence of the nanoparticle delivered drug (bright green dots) was seen only in the tumors of the nine patients investigated, and not in their adjacent healthy tissue. Credit: Courtesy of the M. E. Davis Laboratory/Caltech |
Abstract:
A team of researchers led by Caltech scientists have shown that nanoparticles can function to target tumors while avoiding adjacent healthy tissue in human cancer patients.
Nanoparticle-based cancer therapies shown to work in humans
Pasadema. CA | Posted on March 21st, 2016"Our work shows that this specificity, as previously demonstrated in preclinical animal studies, can in fact occur in humans," says study leader Mark E. Davis, the Warren and Katharine Schlinger Professor of Chemical Engineering at Caltech. "The ability to target tumors is one of the primary reasons for using nanoparticles as therapeutics to treat solid tumors."
The findings, published online the week of March 21, 2016 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, demonstrate that nanoparticle-based therapies can act as a "precision medicine" for targeting tumors while leaving healthy tissue intact.
In the study, Davis and his colleagues examined gastric tumors from nine human patients both before and after infusion with a drug -- camptothecin -- that was chemically bound to nanoparticles about 30 nanometers in size.
"Our nanoparticles are so small that if one were to increase the size to that of a soccer ball, the increase in size would be on the same order as going from a soccer ball to the planet Earth," says Davis, who is also a member of the City of Hope Comprehensive Cancer Center in Duarte, California, where the clinical trial was conducted.
The team found that 24 to 48 hours after the nanoparticles were administered, they had localized in the tumor tissues, released their drug cargo, and the drug had the intended biological effects of inhibiting two proteins that are involved in the progression of the cancer. Equally important, both the nanoparticles and the drug were absent from healthy tissue adjacent to the tumors.
The nanoparticles are designed to be flexible delivery vehicles. "We can attach different drugs to the nanoparticles, and by changing the chemistry of the bond linking the drug to the nanoparticle, we can alter the release rate of the drug to be faster or slower," says Andrew Clark, a graduate student in Davis's lab and the study's first author.
Davis says his team's findings are suggestive that a phenomenon known as the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect is at work in humans. In the EPR effect, abnormal blood vessels that are "leakier" than normal blood vessels in healthy tissue allow nanoparticles to preferentially concentrate in tumors. Until now, the existence of the EPR effect has been conclusively proven only in animal models of human cancers.
"Our results don't prove the EPR effect in humans, but they are completely consistent with it," Davis says.
The findings could also help pave the way toward more effective cancer drug cocktails that can be tailored to fight specific cancers and that leave patients with fewer side effects.
"Right now, if a doctor wants to use multiple drugs to treat a cancer, they often can't do it because the cumulative toxic effects of the drugs would not be tolerated by the patient," Davis says. "With targeted nanoparticles, you have far fewer side effects, so it is anticipated that drug combination can be selected based on the biology and medicine rather than the limitations of the drugs."
In addition to Davis and Clark, other coauthors on the study, entitled "CRLX101 nanoparticles localize in human tumors and not in adjacent, nonneoplastic tissue after intravenous dosing," include Devin Wiley (MS '11, PhD '13) and Jonathan Zuckerman (PhD '12); Paul Webster of the Oak Crest Institute of Science; Joseph Chao and James Lin at City of Hope; and Yun Yen of Taipei Medical University, who was at City of Hope and a visitor in the Davis lab at the initiation of the clinical trial.
The research was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health and by Cerulean Pharma Inc. Davis is a consultant to and holds stock in Cerulean Pharma Inc.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Deborah Williams-Hedges
626-395-3227
Copyright © California Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








