Home > Press > Kellogg researchers develop new nanoparticle with potential to treat ocular cancer: Using nanoparticles to kill tumor cells inside the eye
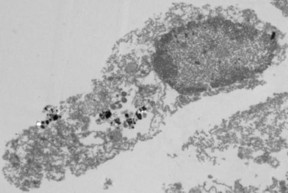 |
| Disruption of the tumor cell due to treatment
with nanoparticles and visible light. iStock_eye care_Medium.jpg |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of Michigan Kellogg Eye Center have developed a new nanoparticle that uses a tumor cell's protective mechanism against itself -- short-circuiting tumor cell metabolism and killing tumor cells.
Kellogg researchers develop new nanoparticle with potential to treat ocular cancer: Using nanoparticles to kill tumor cells inside the eye
Ann Arbor, MI | Posted on February 19th, 2016"Our work uses a semiconducting nanoparticle with an attached platinum electrode to drive the synthesis of an anti-cancer compound when illuminated by light," says Howard R. Petty, Ph.D., professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences and of microbiology and immunology. "The nanoparticle mimics the behavior of NADPH oxidase, an enzyme used by immune cells to kill tumor cells and infectious agents. Since tumor cells typically use NADPH to protect themselves from toxins, the more NADPH they synthesize for protection, the faster they die."
In a four-year study conducted on the mouse model in advanced breast cancer metastasis in the eye's anterior chamber, Petty and colleagues found that the new nanoparticle not only killed tumor cells in the eye, but also extended the survival of experimental mice bearing 4T1 tumors, a cell line that is extremely difficult to kill. "Previous monotherapies have not extended the lifetimes of mice bearing this type of tumor," Petty said. "Our work has shown that we can extend survival of the mice."
The findings of the Kellogg team are detailed in a new paper published in Nanotechnology on Feb. 19. Joining Petty as co-authors of the paper are research associate Andrea J. Clark, and undergraduates Emma L. Coury and Alexandra M. Meilhac.
"This treatment offers many advantages," Petty says. "The nanoparticle produces about 20 million toxins per hour in each cell. Also, the nanoparticle is activated by light, so it can be turned on and off simply by exposing it to the correct color of visible light."
This nanotechnology also has the potential to be used for multiple applications in ophthalmology and other disciplines.
###
Reference: WO3/Pt nanoparticles are NADPH oxidase biomimetics that mimic effector cells in vitro and in vivo Andrea J Clark, Emma L Coury, Alexandra M Meilhac and Howard R Petty. Nanotechnology, February 19, 2016.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Barbara Wylan Sefton
734-763-6967
Copyright © University of Michigan Health System
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








