Home > Press > Metal oxide sandwiches: New option to manipulate properties of interfaces
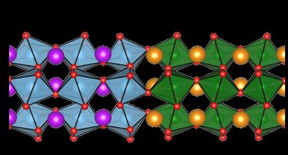 |
| This is a sketch of the structure of both metal oxide layers. Interesting new properties can arise at the interface.
Credit: M. Bibes |
Abstract:
Sandwich systems of thin film transition metal oxides display surprising properties at their interfaces. In case of the paradigmatic example of Lanthan-Aluminate ( LaAlO3) and Strontium-Titanate (SrTiO3) both materials are insulators and non-magnetic, while their interface has been observed to display ferromagnetism, high electrical conductivity and even superconductivity.
Metal oxide sandwiches: New option to manipulate properties of interfaces
Berlin, Germany | Posted on February 8th, 2016Now the team of Manuel Bibes, CNRS Thales at Palaiseau, France, in collaboration with scientists at HZB around Sergio Valencia and several European groups, devised a new approach to tailor interface properties. Together they designed a series of experiments at the synchrotron source BESSY II to shed more light on the emergence of such property changes, identifying a new "knob" for their control.
Rare-Earth Elements influence charge transfer
The samples, which the team of Manuel Bibes did produce, consisted of a sandwich of 2 nm Gadolinium-Titanate (GdTiO3) and "R"-Nickelate (RNiO3) films, where R is a rare-earth element. "We have been able to combine two very different transition metal oxides: whereas in the titanate electrons in the chemical bonds are strongly localized around the ions, in the nickelate side these electrons are shared between Nickel- and Oxygen-ions, and thus highly covalent", Manuel Bibes explains. When putting both materials together some charge is transferred from the titanate layer to the nickelate one. They investigated this charge transfer process for samples containing different rare-earth elements in the nickelate layer such as Lanthanum, Neodymium and Samarium at BESSY II.
Their results show that the charge transfer at the interface between the materials strongly depends on the rare earth element in the nickelate layer. Different rare-earth elements have different atomic radii (size).This modifies the interaction between the Ni and O atoms and the degree of "covalency" between Ni and O changes. This was already known, but now the scientists have observed that this also affects the charge transferred from the GdTiO3 to the Nickelate film. "This is the key result", Sergio Valencia from HZB explains. "We have found a new "knob". Covalency (which is controlled by changing R) controls the charge transfer between the titanate and the nickelate."
Ferromagnetism observed, superconductivity still searched
Tuning the charge transfer in this way might allow to control the formation of new interfacial phases too. For example, the scientists observed a new ferromagnetic phase at the interface. "Our work may help in the ongoing quest for cuprate-like superconductivity in nickelate heterostructures", Valencia says. "We hope that this study will help to design better interfaces for exploring new exciting new phases of matter at interfaces between covalent materials", Bibes adds.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Sergio Valencia Molina
49-308-062-15619
Copyright © Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Published in Nature Physics: doi:10.1038/nphys3627
Published in Nature Physics: doi:10.1038/nphys3627
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








