Home > Press > Visualizing atoms of perovskite crystals: OIST researchers conduct the first atomic resolution study of perovskites used in next generation solar cells
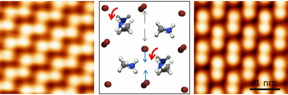 |
| Methylammonium molecules (represented by a ball-and-stick model in the centre) in methylammonium lead bromide (CH3NH3PbBr3) can rotate. They favour specific orientations that lead to two types of surface structures with distinctly different properties (left and right images). CREDIT: OIST |
Abstract:
Organic-inorganic perovskite materials are key components of the new generation of solar cells. Understanding properties of these materials is important for improving lifetime and quality of solar cells. Researchers from the Energy Materials and Surface Sciences (EMSS) Unit, led by Prof. Yabing Qi, at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) in collaboration with Prof. Youyong Li's group from Soochow University (China) and Prof. Nam-Gyu Park's group from Sungkyunkwan University (Korea) report in the Journal of the American Chemical Society the first atomic resolution study of organic-inorganic perovskite.
Visualizing atoms of perovskite crystals: OIST researchers conduct the first atomic resolution study of perovskites used in next generation solar cells
Okinawa, Japan | Posted on January 11th, 2016Perovskites are a class of materials with the general chemical formula ABX3. A and B are positive ions bound by negative ions X. Organic-inorganic perovskites used in solar cells are usually methylammonium lead halides (CH3NH3PbX3, where X is bromine, iodine, or chlorine). The OIST scientists used a single crystal of methylammonium lead bromide (CH3NH3PbBr3) to create topographic images of its surface with a scanning tunneling microscope.
This microscope uses a conducting tip that moves across the surface in a manner very similar to a finger moving across a Braille sign. While the bumps in Braille signs are a few millimetres apart, the microscope detects bumps that are more than million times smaller -- atoms and molecules. This is achieved by the quantum tunneling effect -- the ability of an electron to pass through a barrier. The probability of an electron passing between the material surface and the tip depends on the distance between the two. The resulting atomic-resolution topographic images reveal positions and orientations of atoms and molecules, and also provide a detailed look at structural defects in the surface.
"At room temperature atoms and molecules are quite mobile, so we decided to freeze the crystal to almost absolute zero (-269�C) to get a good picture of its atomic structure," says Dr Robin Ohmann, a member of the EMSS Unit and the first author of the paper. The crystal was cut and studied in a vacuum to avoid contamination of the surface. Dr Ohmann's colleagues from Soochow University calculated atomic structures using principles of quantum physics and then compared them with scanning tunneling microscopy data.
The researchers discovered that methylammonium molecules can rotate and that they favour specific orientations that lead to two types of surface structures with distinctly different properties. Apart from rotation, these molecules affect positions of neighbouring bromine ions, further altering the atomic structure. Since the structure dictates the electronic properties of the material, the geometric positions of atoms are essential for understanding of solar cells.
Scanning tunneling microscope images also reveal local imperfections caused by dislocations of molecules and ions and, probably, missing atoms. These imperfections may affect device performance, for example, by changing electrical properties such as conductivity.
The structure of perovskite materials is temperature-sensitive and the observed structure of the frozen crystal might not be fully identical to the structure at room temperature. However, the comprehensive description of perovskite crystals at the atomic level paves the way to better understanding of their behaviour under real-life conditions. The current findings shed light on molecule-ion interplay on the surface of an organic-inorganic crystal and should help to improve designs of future solar cells. The next goal of the researchers is to examine interactions between perovskites and other molecules, for example water molecules that are known to interfere with the performance of solar cells.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kaoru Natori
81-989-662-389
Copyright © Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate Univers
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








