Home > Press > A new way to deliver microRNAs for cancer treatment: Scientists exploit gene therapy to shrink tumors in mice with an aggressive form of breast cancer
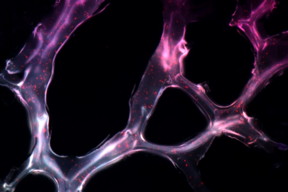 |
| MIT researchers developed this hydrogel embedded with triple helix microRNA particles and used it to treat cancer in mice.
Image: João Conde, Nuria Oliva, and Natalie Artzi |
Abstract:
Twenty years ago, scientists discovered that short strands of RNA known as microRNA help cells to fine-tune their gene expression. Disruption or loss of some microRNAs has been linked to cancer, raising the possibility of treating tumors by adjusting microRNA levels.
A new way to deliver microRNAs for cancer treatment: Scientists exploit gene therapy to shrink tumors in mice with an aggressive form of breast cancer
Cambridge, MA | Posted on January 10th, 2016Developing such treatments requires delivering microRNA to tumors, which has proven difficult. However, researchers from MIT have now shown that by twisting RNA strands into a triple helix and embedding them in a biocompatible gel, they can not only deliver the strands efficiently but also use them to shrink aggressive tumors in mice.
Using this technique, the researchers dramatically improved cancer survival rates by simultaneously turning on a tumor-suppressing microRNA and de-activating one that causes cancer. They believe their approach could also be used for delivering other types of RNA, as well as DNA and other therapeutic molecules.
“This is a platform that can deliver any gene of interest,” says Natalie Artzi, a research scientist in MIT’s Institute for Medical Engineering and Science (IMES) and an assistant professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. “This work demonstrates the promise of local delivery in combating cancer. In particular, as relates to gene therapy, the triplex structure improves RNA stability, uptake, and transfection efficacy.”
Artzi is the senior author of a paper describing the technique in the Dec. 7 issue of Nature Materials. The study’s lead author is IMES postdoc João Conde.
Local delivery
The new technique reflects a shift among cancer researchers toward designing more targeted and selective treatments, Artzi says. “Cancer is perceived as a systemic disease that mandates systemic treatment. However, in some cases, solid tumors can benefit from a local therapy that may include gene therapy or chemotherapy,” she says.
To create their new system, the researchers took advantage of a material previously developed by Artzi and her colleagues, made from two polymers known as dextran and dendrimer, as a tissue glue.
In the new study, Artzi and Conde exploited the ability of dendrimer to form a self-assembled structure with the microRNAs of interest. First, they wound three strands of microRNA together in a triple helix, creating a molecule that is much more stable than a single or double RNA strand. These triplexes then bind to dendrimer molecules, some of which form nanoparticles, and when dextran is added the injectable formulation gels on top of the solid tumor.
Once placed on the tumor, the gel slowly releases microRNA-dendrimer particles, which are absorbed into the tumor cells. After the particles enter the cells, enzymes cut each triple helix into three separate microRNA strands.
MicroRNA alters gene expression by disrupting messenger RNA molecules, which carry DNA’s instructions to cells’ protein-building machinery. The human genome is believed to encode more than 1,000 microRNAs, and many of these can cause disease when not working properly.
In this study, the researchers delivered two targeted microRNA sequences, plus a third strand whose only function is to keep the helix stable. One of the strands mimics the actions of a naturally occurring microRNA called miR-205, which is frequently silenced in cancer cells. The other blocks a microRNA called miR-221, which is often overactive in cancer cells.
The researchers tested the microRNA delivery platform in mice implanted with triple-negative breast tumors, which lack the three most common breast cancer markers: estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and Her2. Such tumors are usually very difficult to treat.
Treating these mice with microRNA delivered as a triple helix was far more effective than standard chemotherapy treatments, the researchers found. With the triple helix treatment, tumors shrank 90 percent and the mice survived for up to 75 days, compared with less than a week for other treatments (including single and double strands of the same microRNAs).
The microRNA combination used in this study appears to work by interfering with cancer cells’ ability to grow and to stick to other cells, the researchers found.
“This is a great proof of principle,” says Mauro Ferrari, the president and CEO of the Houston Methodist Research Institute, who was not involved in the study. “In many ways microRNA is the ultimate opportunity for targeted cancer therapy, but the problem of delivering it has been intractable.”
Identifying targets
Artzi and Conde now plan to look for combinations of microRNA that could combat other types of tumors. This delivery technique will likely work best with accessible solid tumors, such as breast, colon, and possibly brain tumors, Artzi says.
This type of microRNA therapy could also be used to prevent tumors from spreading throughout the body. Several microRNA sequences have already been found to play a role in this process, known as metastasis.
“There are so many microRNAs that are involved in metastasis. It’s really an underexplored field,” Conde says.
The researchers are also looking into using this technique for delivering other types of nucleic acids, including short interfering RNA for RNA interference and DNA for gene therapy. “We really want to identify the right targets and use this platform to deliver them in a very effective way,” Artzi says.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








