Home > Press > New research could help build better fighter planes and space shuttles
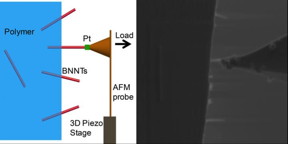 |
| Researchers tested the force required to pluck a boron nitride nanotube (BNNT) from a polymer by welding a cantilever to the nanotube and pulling. The experimental set-up is shown in a schematic on the left and an actual image on the right. CREDIT: Changhong Ke, Binghamton University |
Abstract:
Thousands bound together are still thinner than a single strand of human hair, but with research from Binghamton University, boron nitride nanotubes may help build better fighter planes and space shuttles.
New research could help build better fighter planes and space shuttles
Binghamton, NY | Posted on January 4th, 2016A team of scientists led by Changhong Ke, associate professor of mechanical engineering at Binghamton University's Thomas J. Watson School of Engineering and Applied Science, and researcher Xiaoming Chen were the first to determine the interface strength between boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) and epoxy and other polymers.
"We think that this could be the first step in a process that changes the way we design and make materials that affect the future of travel on this planet and exploration of other worlds beyond our own," said Ke. "Those materials may be way off still, but someone needed to take the first step, and we have."
Ke's group found that BNNTs in polymethyl metacrylate (PMMA) form much stronger interfaces than comparable carbon tubes with the same polymer. Furthermore, BNNT-epoxy interfaces are even stronger. A stronger interface means that a larger load can be transferred from the polymer to nanotubes, a critical characteristic for superior mechanical performance of composite materials. Future airplane wings and spacecraft hulls built of those BNNT composite materials could be lighter and more fuel efficient, while maintaining the strength needed to withstand the rigors of flight.
Since nanotube wall thickness and diameters are measured in billionths of a meter, Ke and Chen extracted single BNNTs from a piece of epoxy and then repeated the process with PMMA inside an electron microscope. Their conclusions were based on the amount of force needed to do the extractions. This was the first time that BNNTs --more chemically and thermally stable than the more common carbon nanotubes (CNTs) --were in this kind of experiment. BNNTs can shield space radiation better than CNTs, which would make them an ideal building material for spacecraft.
"They are both light and strong," Ke said of the two kinds of tubes. "They have similar mechanical properties, but different electrical properties. Those differences help to add strength to the BNNT interfaces with the polymers."
Metaphorically, think of the epoxy or other polymer materials with the BNNT nanotubes inside like a piece of reinforced concrete. That concrete gets much of its strength from the makeup of the steel rebar and cement; the dispersion of rebar within the cement; the alignment of rebar within the cement; and "stickiness" of the connection between the rebar and the surrounding cement. The scientists essentially measured the "stickiness" of a single nanotube 'rebar' -- helped by molecular and electrostatic interactions -- by removing it from polymer "cement."
The work was funded by the US Air Force Office of Scientific Research - Low Density Materials program, with materials provided by NASA. Co-authors Xianqiao Wang and graduate student Liuyang Zhang from the University of Georgia provided verification and explanation data through computational simulations after the experiments were conducted in Binghamton.
Catharine Fay from the NASA Langley Research Center and Cheol Park of the Center and the University of Virginia are co-authors on the paper.
In September, Ke and his collaborators received three years of additional funding totaling $815,000 from the Air Force to continue research.
The paper, "Mechanical Strength of Boron Nitride Nanotube-Polymer Interfaces," was published in the latest issue of Applied Physics Letters.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Changhong Ke
607-777-4782
Copyright © Binghamton University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








