Home > Press > How to train your bacterium: Berkeley Lab scientists teach bacterium a new trick for artificial photosynthesis
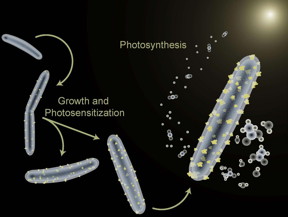 |
| The bacterium Moorella thermoacetica is being used to perform photosynthesis and also to synthesize semiconductor nanoparticles in a hybrid artificial photosynthesis system for converting sunlight into valuable chemical products. CREDIT: Peidong Yang, Berkeley Lab/UC Berkeley |
Abstract:
Trainers of dogs, horses, and other animal performers take note: a bacterium named Moorella thermoacetica has been induced to perform only a single trick, but it's a doozy. Berkeley Lab researchers are using M. thermoacetica to perform photosynthesis - despite being non-photosynthetic - and also to synthesize semiconductor nanoparticles in a hybrid artificial photosynthesis system for converting sunlight into valuable chemical products.
How to train your bacterium: Berkeley Lab scientists teach bacterium a new trick for artificial photosynthesis
Berkeley, CA | Posted on January 4th, 2016"We've demonstrated the first self-photosensitization of a non-photosynthetic bacterium, M. thermoacetica, with cadmium sulfide nanoparticles to produce acetic acid from carbon dioxide at efficiencies and yield that are comparable to or may even exceed the capabilities of natural photosynthesis," says Peidong Yang, a chemist with Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division, who led this work.
"The bacteria/inorganic-semiconductor hybrid artificial photosynthesis system we've created is self-replicating through the bio-precipitation of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles, which serve as the light harvester to sustain cellular metabolism," Yang says. "Demonstrating this cyborgian ability to self-augment the functionality of biological systems through inorganic chemistry opens up the integration of biotic and abiotic components for the next generation of advanced solar-to-chemical conversion technologies."
Yang, who also holds appointments with UC Berkeley and the Kavli Energy NanoScience Institute (Kavli-ENSI) at Berkeley, is the corresponding author of a paper describing this research in Science. The paper is titled "Self-photosensitization of non-photosynthetic bacteria for solar-to-chemical production." Co-authors are Kelsey Sakimoto and Andrew Barnabas Wong.
Photosynthesis is the process by which nature harvests sunlight and uses the solar energy to synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water. Artificial versions of photosynthesis are being explored for the clean, green and sustainable production of chemical products now made from petroleum, primarily fuels and plastics. Yang and his research group have been at the forefront of developing artificial photosynthetic technologies that can realize the full potential of solar-to-chemical synthesis.
"In our latest study, we combined the highly efficient light harvesting of an inorganic semiconductor with the high specificity, low cost, and self-replication and self-repair of a biocatalyst," Yang says. "By inducing the self-photosensitization of M. thermoacetica with cadmium sulfide nanoparticles, we enabled the photosynthesis of acetic acid from carbon dioxide over several days of light-dark cycles at relatively high quantum yields, demonstrating a self-replicating route toward solar-to-chemical carbon dioxide reduction."
Cadmium sulfide is a well-studied semiconductor with a band structure and that is well-suited for photosynthesis. As both an "electrograph" (meaning it can undergo direct electron transfers from an electrode), and an "acetogen" (meaning it can direct nearly 90-percent of its photosynthetic products towards acetic acid), M. thermoacetica serves as the ideal model organism for demonstrating the capabilities of this hybrid artificial photosynthesis system.
"Our hybrid system combines the best of both worlds: the light-harvesting capabilities of semiconductors with the catalytic power of biology," Yang says. "In this study, we've demonstrated not only that biomaterials can be of sufficient quality to carry out useful photochemistry, but that in some ways they may be even more advantageous in biological applications."
###
This work was funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Office of Science. The interface design part of the study was carried out the Molecular Foundry, a DOE Office Science User Facility hosted by Berkeley Lab.
####
About Berkeley Lab
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world's most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit the Office of Science website at science.energy.gov/.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Yarris
510-486-5375
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








