Home > Press > Columbia engineers build biologically powered chip: System combines biological ion channels with solid-state transistors to create a new kind of electronics
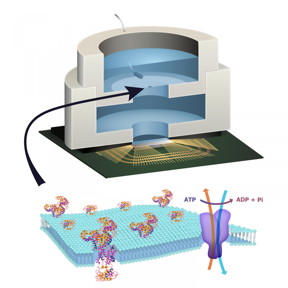 |
| Illustration depicting biocell attached to CMOS integrated circuit with membrane containing sodium-potassium pumps in pore. CREDIT: Trevor Finney and Jared Roseman/Columbia Engineering |
Abstract:
Columbia Engineering researchers have, for the first time, harnessed the molecular machinery of living systems to power an integrated circuit from adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of life. They achieved this by integrating a conventional solid-state complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuit with an artificial lipid bilayer membrane containing ATP-powered ion pumps, opening the door to creating entirely new artificial systems that contain both biological and solid-state components. The study, led by Ken Shepard, Lau Family Professor of Electrical Engineering and professor of biomedical engineering at Columbia Engineering, is published online Dec. 7 in Nature Communications.
Columbia engineers build biologically powered chip: System combines biological ion channels with solid-state transistors to create a new kind of electronics
New York, NY | Posted on December 7th, 2015"In combining a biological electronic device with CMOS, we will be able to create new systems not possible with either technology alone," says Shepard. "We are excited at the prospect of expanding the palette of active devices that will have new functions, such as harvesting energy from ATP, as was done here, or recognizing specific molecules, giving chips the potential to taste and smell. This was quite a unique new direction for us and it has great potential to give solid-state systems new capabilities with biological components."
Shepard, whose lab is a leader in the development of engineered solid-state systems interfaced to biological systems, notes that despite its overwhelming success, CMOS solid-state electronics is incapable of replicating certain functions natural to living systems, such as the senses of taste and smell and the use of biochemical energy sources. Living systems achieve this functionality with their own version of electronics based on lipid membranes and ion channels and pumps, which act as a kind of 'biological transistor.' They use charge in the form of ions to carry energy and information -- ion channels control the flow of ions across cell membranes. Solid-state systems, such as those in computers and communication devices, use electrons; their electronic signaling and power are controlled by field-effect transistors.
In living systems, energy is stored in potentials across lipid membranes, in this case created through the action of ion pumps. ATP is used to transport energy from where it is generated to where it is consumed in the cell. To build a prototype of their hybrid system, Shepard's team, led by PhD student Jared Roseman, packaged a CMOS integrated circuit (IC) with an ATP-harvesting 'biocell.' In the presence of ATP, the system pumped ions across the membrane, producing an electrical potential harvested by the IC.
"We made a macroscale version of this system, at the scale of several millimeters, to see if it worked," Shepard notes. "Our results provide new insight into a generalized circuit model, enabling us to determine the conditions to maximize the efficiency of harnessing chemical energy through the action of these ion pumps. We will now be looking at how to scale the system down."
While other groups have harvested energy from living systems, Shepard and his team are exploring how to do this at the molecular level, isolating just the desired function and interfacing this with electronics. "We don't need the whole cell," he explains. "We just grab the component of the cell that's doing what we want. For this project, we isolated the ATPases because they were the proteins that allowed us to extract energy from ATP."
The ability to build a system that combines the power of solid-state electronics with the capabilities of biological components has great promise. "You need a bomb-sniffing dog now, but if you can take just the part of the dog that is useful -- the molecules that are doing the sensing -- we wouldn't need the whole animal," says Shepard.
"With appropriate scaling, this technology could provide a power source for implanted systems in ATP-rich environments such as inside living cells," added Roseman.
###
The work is funded by the Keck Foundation and the Office of Naval Research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Holly Evarts
347-453-7408
Copyright © Columbia University School of Engineering and Applied Scienc
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Homeland Security
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
![]() Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








