Home > Press > Guided ultrasound plus nanoparticle chemotherapy cures tumors in mice
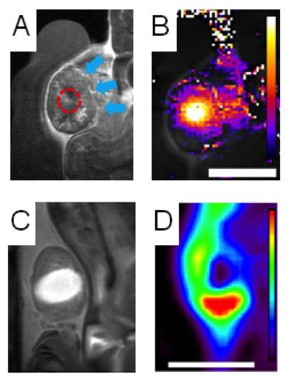 |
| Clockwise from top left: A tumor (blue arrows) is heated with ultrasound (red dashed line); heat map of tumor during treatment; PET scan shows nanoparticles in surviving tumor margin; bright contrast agent shows area damaged by heat. CREDIT: Andrew Wong/UC Davis |
Abstract:
Thermal ablation with magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound surgery (MRgFUS) is a noninvasive technique for treating fibroids and cancer. New research from UC Davis shows that combining the technique with chemotherapy can allow complete destruction of tumors in mice.
Guided ultrasound plus nanoparticle chemotherapy cures tumors in mice
Davis, CA | Posted on December 5th, 2015MRgFUS combines an ultrasound beam that heats and destroys tissue with a magnetic resonance imaging to guide the beam and monitor the effects of treatment. The effectiveness of the treatment can be limited by the need to spare normal tissue or critical structures on the tumor margins, as well as the need to eliminate micrometastases.
In a new paper in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, Katherine W. Ferrara, distinguished professor of biomedical engineering at UC Davis, and colleagues report on a strategy that can destroy an entire tumor without thermal destruction of the tumor margin. Her group demonstrated a dramatic increase in the concentration of anti-cancer chemotherapy within several types of MRgFUS thermal ablation-treated tumors.
"MRgFUS is already FDA approved for the treatment of uterine fibroids and palliation of bone metastases. We hope to expand the indication for MRgFUS by supplementing it with chemotherapy," said first author Andrew Wong, a graduate student with the UC Davis Physician Scientist Training Program.
Ferrara's previous research has shown that ultrasound-induced mild hyperthermia can enhance the accumulation of tiny nanoparticles carrying anti-cancer drugs, but the accumulation is dependent on the type of tumor. Her group hypothesized that combining thermal ablation and chemotherapy could improve efficacy across multiple types of tumors.
The team used a variety of techniques including combined positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET-CT), magnetic resonance imaging, autoradiography, and fluorescence imaging to track nanoparticles loaded with the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin in a mouse model of breast cancer.
They found that as the ultrasound damaged the tumor and induced a local immune response, nanoparticles accumulated in the tumor and the local drug concentration increased 50-fold. The high drug concentrations continued over several weeks, increasing total exposure of the tumor to the drug.
Ferrara's research team found that the enhanced drug accumulation induced by MRgFUS resulted in improved survival and a consistent cure in their preclinical model of breast cancer, even when part of the tumor was left intact.
They also demonstrated that an effective cure could be achieved with a carefully designed protocol involving heat-activated nanoparticles, which, when gently heated by ultrasound, release their chemotherapeutic payload in the vasculature surrounding the tumor.
###
Additional members of the team included Brett Z. Fite, Yu Liu, Josquin Foiret, Azadeh Kheirolomoom, Jai W. Seo, Katherine D. Watson, Lisa M. Mahakian, Sarah Tam and Alexander D. Borowsky. The work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andy Fell
530-752-4533
Copyright © University of California, Davis
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








