Home > Press > Scientists 'see' detailed make-up of deadly toxin for the first time: Exciting advance provides hope for developing novel potential method of treating pneumococcal diseases such as bacterial pneumonia, meningitis and septicaemia
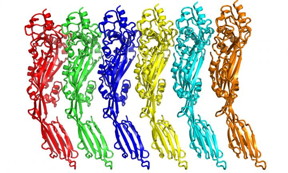 |
| Figure shows the way that copies of the toxin pack together to form pores in cells. CREDIT: University of Leicester |
Abstract:
Scientists from the University of Leicester have for the first time created a detailed image of a toxin - called pneumolysin - associated with deadly infections such as bacterial pneumonia, meningitis and septicaemia.
Scientists 'see' detailed make-up of deadly toxin for the first time: Exciting advance provides hope for developing novel potential method of treating pneumococcal diseases such as bacterial pneumonia, meningitis and septicaemia
Leicester, UK | Posted on November 25th, 2015The three-year study involving four research groups from across the University has been described as an exciting advance because it points to the possibility of creating therapeutics that block assembly of pneumolysin pores to treat people with pneumococcal disease. The University has recently set up a company Axendos Therapeutics to pursue this aim.
Using a technique called X-ray crystallography at Diamond Light Source, the UK's national synchrotron science facility, the Leicester team was able to see the individual atoms of the toxin. The structure not only reveals what the toxin looks like, but also shows how it assembles on the surface of cells to form lethal pores.
Funded by the Wellcome Trust and the Medical Research Council, the University of Leicester research published in Scientific Reports was led by Professor Russell Wallis of the Departments of Infection, Immunity and Inflammation and Molecular and Cell Biology and Professor Peter Andrew, Head of Department of Infection, Immunity and Inflammation.
Professor Wallis said: "Our research is about a toxin called pneumolysin produced by a bacterium called pneumococcus (aka Streptococcus pneumoniae). Pneumococcal infections are the leading cause of bacterial pneumonia as well as the cause of a range of other life-threatening diseases such as meningitis and septicaemia. Pneumolysin is instrumental in the ability of pneumococcus to cause disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that more than 1.6 million people die every year from pneumococcal infections, including more than 800,000 children under 5 years old.
"The aim of the research was to find out how pneumolysin kills our cells, thereby causing tissue damage and contributing to disease. In particular we wanted to find out how multiple copies of the toxin assemble on the surface of cells.
"We managed to determine the structure of pneumolysin using a technique called X-ray crystallography, which enables us to see the individual atoms of the toxin. The structure not only reveals what the toxin looks like, but also shows how it assembles to form lethal pores.
"Ours is the first detailed structure of pneumolysin. This level of detail is important and useful because it enables us to begin to understand how the toxin works. For example, we can see which parts of the toxin come together during pore assembly. When we disrupt these contacts, the toxin becomes inactivated so can no longer kill cells.
"The mode of action of pneumolysin action revealed by our work appears to be conserved in related toxins from other disease-causing bacteria e.g. toxins produced by pathogenic species of Listeria."
Professor Andrew said: "The determination of the structure of pneumolysin is a thrilling achievement that, worldwide, scientists have been pursuing for more than twenty years. It also offers the real prospect of enhancing our ability to find new drugs for treatment of pneumococcal diseases. Because of fears of antibiotic resistance, researchers have been trying for decades to find new antimicrobial drugs but with little success. A new approach is to identify new targets for therapy and our work over a long period shows that pneumolysin is an excellent target for new treatments. The University of Leicester set up a spin-out company to find drugs that target the toxin. Now the determination of the toxin's structure is an important advance towards achieving this objective."
Professor Wallis said: "The work is especially exciting because of the importance of pneumolysin towards pneumococcal disease and the devastating consequences of pneumococcal infections. Our work has provided new insight into how the toxin kills cells. Much of the experimental work was carried out by two PhD students: Jamie Marshall, who has just completed his PhD and Bayan Faraj, who is in the final year of her project. Overall it has been a real collaborative effort between four research groups across the College of Medicine, Biological Sciences and Psychology involving the groups in the Department of Infection, Immunity and Inflammation as well as the groups of Prof Peter Moody and Dr El-Mezgueldi in the Department of Molecular and Cell Biology."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Wallis
44-011-625-25089
Copyright © University of Leicester
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








