Home > Press > From nanocrystals to earthquakes, solid materials share similar failure characteristics
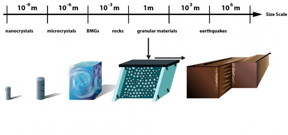 |
| When solid materials such as nanocrystals, bulk metallic glasses, rocks, or granular materials are slowly deformed by compression or shear, they slip intermittently with slip-avalanches similar to earthquakes. CREDIT: University of Illinois |
Abstract:
Apparently, size doesn't always matter. An extensive study by an interdisciplinary research group suggests that the deformation properties of nanocrystals are not much different from those of the Earth's crust.
From nanocrystals to earthquakes, solid materials share similar failure characteristics
Urbana, IL | Posted on November 19th, 2015"When solid materials such as nanocrystals, bulk metallic glasses, rocks, or granular materials are slowly deformed by compression or shear, they slip intermittently with slip-avalanches similar to earthquakes," explained Karin Dahmen, a professor of physics at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. "Typically these systems are studied separately. But we found that the scaling behavior of their slip statistics agree across a surprisingly wide range of different length scales and material structures."
"Identifying agreement in aspects of the slip statistics is important, because it enables us to transfer results from one scale to another, from one material to another, from one stress to another, or from one strain rate to another," stated Shivesh Pathak, a physics undergraduate at Illinois, and a co-author of the paper, "Universal Quake Statistics: From Compressed Nanocrystals to Earthquakes," appearing in Scientific Reports. "The study shows how to identify and explain commonalities in the deformation mechanisms of different materials on different scales.
"The results provide new tools and methods to use the slip statistics to predict future materials deformation," added Michael LeBlanc, a physics graduate student and co-author of the paper. "They also clarify which system parameters significantly affect the deformation behavior on long length scales. We expect the results to be useful for applications in materials testing, failure prediction, and hazard prevention."
Researchers representing a broad a range of disciplines--including physics, geosciences, mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, and materials science--from the United States, Germany, and the Netherlands contributed to the study, comparing five different experimental systems, on several different scales, with model predictions.
As a solid is sheared, each weak spot is stuck until the local shear stress exceeds a random failure threshold. It then slips by a random amount until it re-sticks. The released stress is redistributed to all other weak spots. Thus, a slipping weak spot can trigger other spots to fail in a slip avalanche.
Using tools from the theory of phase transitions, such as the renormalization group, one can show that the slip statistics of the model do not depend on the details of the system.
"Although these systems span 13 decades in length scale, they all show the same scaling behavior for their slip size distributions and other statistical properties," stated Pathak. "Their size distributions follow the same simple (power law) function, multiplied with the same exponential cutoff."
The cutoff, which is the largest slip or earthquake size, grows with applied force for materials spanning length scales from nanometers to kilometers. The dependence of the size of the largest slip or quake on stress reflects "tuned critical" behavior, rather than so-called self-organized criticality, which would imply stress-independence.
"The agreement of the scaling properties of the slip statistics across scales does not imply the predictability of individual slips or earthquakes," LeBlanc said. "Rather, it implies that we can predict the scaling behavior of average properties of the slip statistics and the probability of slips of a certain size, including their dependence on stress and strain-rate."
###
Study co-authors include Jonathan Uhl, Xin Liu, Ryan Swindeman, Nir Friedman, University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign; Danijel Schorlemmer and Georg Dresen, German Research Centre for Geosciences; Danijel Schorlemmer and Thorsten Becker, University of Southern California; Robert Behringer, Duke University; Dmitry Denisov and Peter Schall, University of Amsterdam; Xiaojun Gu, Wendelin J. Wright, Xiaojun Gu and Wendelin J. Wright, Bucknell University; Todd Hufnagel, Johns Hopkins University; Andrew Jennings and Julia R. Greer, California Institute of Technology; and P.K. Liaw, The University of Tennessee; Georgios Tsekenis, Harvard, and Braden Brinkman, Seattle, were part of Dahmen's research group during the original study.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Karin Dahmen
217-244-8873
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








