Home > Press > Nanotweezer is new tool to create advanced plasmonic technologies
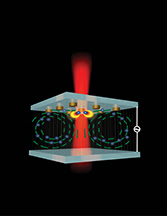 |
| This rendering depicts a new type of "nanotweezer" that could aid efforts to create advanced technologies such as quantum computers and ultra-high-resolution displays. Purdue University image/Mikhail Shalaginov and Pamela Burroff-Murr |
Abstract:
Long-range and rapid transport of individual nanoobjects by a hybrid electrothermoplasmonic nanotweezer
Justus C. Ndukaife1,2, Alexander V. Kildishev1, Agbai George Agwu Nnanna2, Vladimir M. Shalaev1, Steven T. Wereley3 and Alexandra Boltasseva1,4*
1School of Electrical & Computer Engineering and Birck Nanotechnology Center, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907, USA. 2Water Institute, Purdue University Calumet, Hammond, Indiana 46323, USA. 3School of Mechanical Engineering and Birck Nanotechnology Center, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907, USA. 4DTU Fotonik, Department of Photonics Engineering, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby DK-2800, Denmark. *email:
Plasmon-enhanced optical trapping is being actively studied to provide efficient manipulation of nanometer-sized objects. However, a long-standing issue with previously proposed solutions is how to controllably load the trap on-demand without relying on Brownian diffusion. Here, we show that the photo-induced heating of a nanoantenna in conjunction with an applied a.c. electric field can initiate rapid microscale fluid motion and particle transport with a velocity exceeding 10 μms –1, which is over two orders of magnitude faster than previously predicted. Our electrothermoplasmonic device enables on-demand long-range and rapid delivery of single nanoobjects to specific plasmonic nanoantennas, where they can be trapped and even locked in place. We also present a physical model that elucidates the role of both heat-induced fluidic motion and plasmonic field enhancement in the plasmon-assisted optical trapping process. Finally, by applying a d.c. field or low-frequency a.c. field (below 10 Hz) while the particle is held in the trap by the gradient force, the trapped nanoobjects can be immobilized into plasmonic hotspots, thereby providing the potential for effective low-power nanomanufacturing on-chip.
Nanotweezer is new tool to create advanced plasmonic technologies
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on November 2nd, 2015 A new type of "nanotweezer" capable of positioning tiny objects quickly and accurately and freezing them in place could enable improved nanoscale sensing methods and aid research to manufacture advanced technologies such as quantum computers and ultra-high-resolution displays.
The device, fabricated at Purdue University's Birck Nanotechnology Center, uses a cylindrical gold "nanoantenna" with a diameter of 320 nanometers, or about 1/300th the width of a human hair. The structures concentrate and absorb light, resulting in "plasmonic hotspots" and making it possible to manipulate nanometer-scale objects suspended in a fluid.
"The proposed approach enables the immediate implementation of a myriad of exciting applications," said Alexandra Boltasseva, associate professor of electrical and computer engineering.
Findings are detailed in a paper appearing online in Nature Nanotechnology Monday (Nov. 2).
Plasmonic devices harness clouds of electrons called surface plasmons to manipulate and control light. Potential applications for the nanotweezer include improved-sensitivity nanoscale sensors and the study of synthetic and natural nanoobjects including viruses and proteins; creation of "nanoassemblies" for plasmonic materials that could enable a host of advanced technologies; ultra-resolution "optofluidic" displays; and plasmonic circuitry for quantum logic units.
The nanotweezer might be used to create devices containing nanodiamond particles or other nanoscale light-emitting structures that can be used to enhance the production of single photons, workhorses of quantum information processing, which could bring superior computers, cryptography and communications technologies.
Conventional computers use electrons to process information. However, the performance might be ramped up considerably by employing the unique quantum properties of electrons and photons, said Vladimir M. Shalaev, co-director of a new Purdue Quantum Center, scientific director of nanophotonics at the Birck Nanotechnology Center and a distinguished professor of electrical and computer engineering.
"The nanotweezer system has been shown to cause convection in fluid on-demand, resulting in micrometer-per-second nanoparticle transport by harnessing a single plasmonic nanoantenna, which until now has been thought to be impossible," said doctoral student Justus C. Ndukaife.
Previous research had shown that convection using a single plasmonic nanoantenna was too weak to induce such a strong convection, below 10 nanometers per second, which cannot result in a net transport of suspended particles.
However, the Purdue researchers have overcome this limitation, increasing the velocity of particle transport by 100 times by applying an alternating current electric field in conjunction with heating the plasmonic nanoantenna using a laser to induce a force far stronger than otherwise possible.
"The local electromagnetic field intensity is highly enhanced, over 200 times, at the plasmonic hotspot," Ndukaife said. "The interesting thing about this system is that not only can we trap particles but also do useful tasks because we have these hotspots. If I bring a particle to the hotspot then I can do measurements, and sensing is enhanced because it is in a hotspot."
The new hybrid nanotweezer combines a near-infrared laser light and an electric field, inducing an "electrothermoplasmonic flow."
"Then, once we turn off the electric field the laser holds the particles in place, so it can operate in two modes. First, the fast transport using alternating current, and then you turn off the electric field and it goes into the plasmonic tweezing mode," he said.
The Purdue researchers are the first to induce electrothermoplasmonic flow using plasmonic structures.
The system also makes it possible to create patterns to project images, potentially for displays with ultra-fine resolution.
The laser traps the particles, making it possible to precisely position them. The technique was demonstrated with polystyrene particles.
The paper was authored by Ndukaife; Alexander V. Kildishev, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering; Agbai George Agwu Nnanna, a professor of mechanical engineering; Shalaev; Steven T. Wereley, a professor of mechanical engineering; and Boltasseva.
The ongoing research is based at the Birck Nanotechnology Center and is funded by the National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer:
Emil Venere
765-494-4709
Sources:
Vladimir Shalaev
765-494-9855
Alexandra Boltasseva
765-494-0301
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








