Home > Press > Patterning oxide nanopillars at the atomic scale by phase transformation
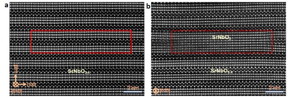 |
| Atomic zip in SrNbO3.4. (a) HAADF STEM image taken before irradiation. The irradiation area is marked by a red open rectangle. (b) HAADF STEM image taken after the electron irradiation for ~300 s showing changes in atomic structure in the irradiated region. The zigzag-like slab in the rectangle is transformed to a chain-like connected structure, resulting in atomic merging of the two neighboring chain-like slabs. The new phase has adopted the structure of SrNbO3. The phase transformation can be well controlled with atomic precision. CREDIT: Nano Letters |
Abstract:
Researchers at Tohoku University's Advanced Institute for Materials Research (AIMR) have carried out a collaborative study aimed at precisely controlling phase transformations with high spatial precision, which represents a significant step forward in realizing new functionalities in confined dimensions.
Patterning oxide nanopillars at the atomic scale by phase transformation
Sendai, Japan | Posted on October 15th, 2015The team, led by Prof. Yuichi Ikuhara, applied the focused electron beam of a scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) to irradiate SrNbO3.4 crystals, and demonstrated a precise control of a phase transformation from layered SrNbO3.4 to perovskite SrNbO3 at the atomic scale.
Such a precise control of phase transformations opens up new avenues for materials design and processing, as well as advanced nanodevice fabrication. Full results of the study have been published in Nano Letters.
Background
Phase transformations in crystalline materials are of primary fundamental interest and practical significance in a wide range of fields, including materials science, information storage and geological science. To date, it remains highly desirable to precisely tailor the phase transformations in a material due to their potential impact on macroscopic properties and thus many advanced applications.
Despite decades of efforts, precisely controlling phase transformations at the atomic scale still poses a significant challenge due to the intricacies of governing thermodynamic conditions with atomic precision. Recent technical advances in aberration-corrected STEM offer fertile new ground for probing samples by a focused sub-Angström electron beam, opening an avenue for precisely triggering phase transformations.
Breakthrough
This work has demonstrated a successful control of a phase transformation from the layered SrNbO3.4 to the perovskite SrNbO3 with atomic precision by manipulating a focused sub-Angström electron beam to any selectable region.
Such a concept - of a precise control of phase transformations with an atomic spatial precision - should be, in principle, applicable not only to SrNbO3.4/SrNbO3 but also to other materials, finding applications in material processing and nanodevice fabrication.
Key points :
Precisely controlling phase transformation with high spatial precision
Patterning oxide nanopillars at the atomic scale by phase transformation
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
For information about the research:
Prof. Yuichi Ikuhara
Advanced Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University
Institute of Engineering Innovation, The University of Tokyo
Tel: +81 3 5841-7688
Assist. Prof. Chunlin Chen and Assoc. Prof. Zhongchang Wang
Advanced Institute for Materials Research, Tohoku University
Email: chen.chunlinwpi-aimr.tohoku.ac.jp
Tel: +81 22 217-5933
For general enquiries:
Advanced Institute for Materials Research (AIMR), PR & Outreach Office
Tohoku University
Tel: +81 22 217-6146
Copyright © Tohoku University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








