Home > Press > Soft Probing with Optical Tweezers: Freiburg researchers have developed a method for measuring soft, structured surfaces using optical forces
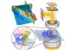 |
| A laser trapping beam (orange) moves the probe (green sphere) over the structured surface (blue spheres), where the beam is displaced depending on the height of the structure. Image: Rohrbach group. |
Abstract:
Surfaces separate outside from inside, control chemical reactions, and regulate the exchange of light, heat, and moisture. They thus play a special role in nature and technology. In the journal Nature Nanotechnology, the Freiburg physicist Prof. Dr. Alexander Rohrbach and his former PhD candidate Dr.. Lars Friedrich have presented an ultra-soft surface scanning method based on an optical trap and optical forces. Microscopy methods like these make it possible to measure particularly sensitive and minuscule structures without destroying them.
Soft Probing with Optical Tweezers: Freiburg researchers have developed a method for measuring soft, structured surfaces using optical forces
Freiburg, Germany | Posted on October 12th, 2015The measuring apparatus is based on a so-called photonic force microscope (PFM) and has the purpose of generating height profiles of soft surfaces like biofilms or cell membranes. It probes a sample up to 5000 times more gently and sensitively than the atomic force microscope (AFM), which is well-established in nanotechnology. An AFM uses a small spring arm - a needle with an ultra-thin tip - to scan a surface. The microscope measures the speed at which the tip moves and uses this information to create a two-dimensional surface profile. In a PFM, the spring arm is replaced by a small plastic sphere that sits at the center of a so-called optical trap and runs along the surface. An optical trap is created by a highly focused laser beam and can be used to hold or move miniscule objects. The sphere is less than 200 nanometers in diameter, making it 500 times thinner than a human hair. The PFM also measures changes in surface height, which displace the sphere from its course, creating a height profile point by point in this way. Although a PFM is not capable of imaging such fine structures as an AFM, it exerts less pressure on the surface, for instance that of a cell, and thus does not deform it. "The basic idea for this technique is actually almost 20 years old," explains Alexander Rohrbach, "but we had to solve a lot of conceptual problems before we could present a practicable and dependable measurement system."
Rohrbach and Friedrich made use of mechanisms that measurement engineers usually try to avoid: scattered light and thermal noise. The tiny plastic sphere, the probe, appears to move in a chaotic manner inside the light trap due to the so-called thermal noise. The optical trap moves the probe along the structured surface, where the probe is displaced depending on the height of the structure. This displacement is detected by the laser beam scattered at the probe. In this way, the three-dimensional position of the probe is measured one million times per second. "The most remarkable thing is that the quivering probe is repeatedly left alone briefly so that the laser beam can jump a step forward for a millisecond," explains Rohrbach. "Once there, the probe records the scattered light from the surface and subtracts it. But before the probe can escape, the laser beam has trapped it again."
Among other things, the Freiburg researchers have used their technique to scan bacteria, which have tiny protrusions on their surface. These so-called pili probably play a role in the communication between bacteria. They react to the softest amount of pressure, and this makes the new technology especially suited to studying them. "In the coming years, we want to scan other and different surfaces by adopting and adapting several measurement principles from the AFM technology," says Rohrbach.
Alexander Rohrbach conducts research at the Department of Microsystems Engineering (IMTEK) and is an associate member of the Cluster of Excellence BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies of the University of Freiburg.
Full bibliographic information
Lars Friedrich, Alexander Rohrbach (2015). Surface imaging beyond the diffraction limit with optically trapped spheres. In: Nature Nanotechnology. doi:10.1038/nnano.2015.202
####
About Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg
The University of Freiburg was founded in 1457 as a classical comprehensive university, making it one of the oldest higher education institutions in Germany. Successful in the Excellence Initiative, the university also boasts an illustrious history with numerous Nobel Prize recipients. Brilliant scholars and creative thinking distinguish it today as a modern top-notch university well equipped for the challenges of the 21st century.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Petra Kränzlein
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








