Home > Press > Laser-wielding physicists seize control of atoms' behavior
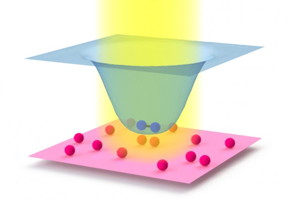 |
| This image shows how a laser (yellow) can affect collisions between atoms (red spheres). The blue spheres depict a molecule. The laser leaves the energy of single atoms unaffected, as represented by the red surface. But the laser lowers the energy of the molecules, leading to the cup-shape of the blue surface. The stronger the laser, the more the two atoms attract each other if they collide inside the laser beam. CREDIT: Chin Group/University of Chicago |
Abstract:
Physicists have wondered in recent years if they could control how atoms interact using light. Now they know that they can, by demonstrating games of quantum billiards with unusual new rules.
Laser-wielding physicists seize control of atoms' behavior
Chicago, IL | Posted on October 5th, 2015In an article published in the Oct. 5 issue of Physical Review Letters, a team of University of Chicago physicists explains how to tune a laser to make atoms attract or repel each other in an exotic state of matter called a Bose-Einstein condensate.
"This realizes a goal that has been pursued for the past 20 years," said Cheng Chin, professor in physics at the University of Chicago, who led the team. "This exquisite control over interactions in a many-body system has great potential for the exploration of exotic quantum phenomena and engineering of novel quantum devices."
Many research groups in the United States and Europe have tried various ideas over the last decade. It was Logan Clark, a graduate student in Chin's group, who came up with the first practical solution. He has now demonstrated the idea in the lab with cesium atoms chilled to temperatures just billionths of a degree above absolute zero, and the technique can be widely applied to other atomic species.
Clark compared the process to a billiards game, when one ball encounters another. "Normally, as soon as the surfaces touch, the balls repel each other and bounce away," Clark said. In Chin's lab, cesium atoms replace the billiard balls, and ordinarily they repel each other when they collide. But by turning up the laser while operating at a "magic" wavelength, Clark showed that the repulsion between atoms can be converted into attraction.
"The atoms exhibit fascinating behavior in this system," he said. By exposing different parts of the sample to different laser intensities, "We can choose to make the atoms attract or repel each other, or pass right through each other without colliding."
Alternatively, by oscillating their interactions, analogous to making the billiard balls rapidly grow and shrink while they roll, the atoms stick to each other in pairs.
The researchers explained two fundamental ways that lasers influence the atomic motion. One is to create potentials, like a bump or valley on the billiard table, proportional to laser intensity. The new way is to alter how billiard balls collide.
"We want our laser to control collisions, but we don't want it to create any hills or valleys," Clark said. When the laser is tuned to a "magic wavelength," the beam creates no hills or valleys, but only affects collisions.
"This is because the magic wavelength happens to be in between two excited states of the atom, so they 'magically' cancel each other out," he said.
Magic is a concept that has no place in science, though the word does enjoy fairly common use among atomic physicists. "Generally it is used to refer to a wavelength at which two effects cancel or are equal, in particular when this cancellation or equality is useful for some technological goal," Clark said.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Steve Koppes
773-702-8366
Copyright © University of Chicago
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








