Home > Press > Researchers create first entropy-stabilized complex oxide alloys
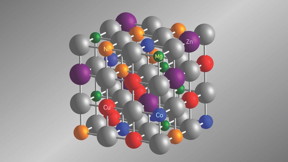 |
| Schematic illustration of an entropy stabilized oxide at the atomic scale. The grey spheres represent the oxygen sub lattice in the rock salt-structured crystal while the colored spheres represent the metal cations. Each different color corresponds to different elemental species. Note that different metals are distributed randomly. Image credit: Jon-Paul Maria. |
Abstract:
“Entropy-Stabilized Oxides”
Authors: Christina M. Rost, Edward Sachet, Trent Borman, Ali Moballegh, Elizabeth C. Dickey, Dong Hou, Jacob L. Jones, and Jon-Paul Maria, North Carolina State University; Stefano Curtarolo, Duke University
Published: online Sept. 29, Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/NCOMMS9485
Abstract: Configurational disorder can be compositionally engineered into mixed oxide by populating a single sublattice with many distinct cations. The formulations promote novel and entropy-stabilized forms of crystalline matter where metal cations are incorporated in new ways. Here, through rigorous experiments, a simple thermodynamic model, and a five-component oxide formulation, we demonstrate beyond reasonable doubt that entropy predominates the thermodynamic landscape, and drives a reversible solid-state transformation between a multi-phase and single-phase state. In the latter, cation distributions are proven to be random and homogeneous. The findings validate the hypothesis that deliberate configurational disorder provides an orthogonal strategy to imagine and discover new phases of crystalline matter and untapped opportunities for property engineering.
Researchers create first entropy-stabilized complex oxide alloys
Raleigh, NC | Posted on September 30th, 2015Researchers from North Carolina State University have created the first entropy-stabilized alloy that incorporates oxides - and demonstrated conclusively that the crystalline structure of the material can be determined by disorder at the atomic scale rather than chemical bonding.
"High entropy materials research has been a hot field since 2007, but no one reported that the unique structure of these materials was indeed stabilized by configurational disorder alone - and no one had created an entropy-stabilized material using anything other than metals," says Jon-Paul Maria, a professor of material science and engineering at NC State and corresponding author of a paper on the new findings.
"While the influence of entropy is present in the natural world - for example, the arrangement of metal ions in feldspar, one of the most common minerals in the Earth's crust - crystalline solids that are stabilized by entropy alone do not exist naturally," Maria says. "We wanted to know if it was possible to stabilize an oxide using entropy and whether we could prove it. The answer was yes to both. Oxides were chosen for this study because they enabled us to directly test this entropy question."
High entropy alloys are materials that consist of four or more elements in approximately equal amounts. More importantly, these elements are distributed randomly at the atomic scale. They have garnered significant attention in recent years because they can have remarkable properties. But to understand entropy-stabilized alloys, you have to understand the crystalline structure of materials.
A material's crystalline structure consists of a repeating arrangement of atoms, which can be different from material to material. That arrangement is called the crystal's "lattice type." For example, think of one crystal as having its atoms arranged as a series of cubes. In a conventional material that contains multiple atom types, the arrangement is regular and ordered. Along one of those cube edges, the atoms would follow a regular repeat pattern. In an entropy-stabilized material, the relative arrangement is completely random.
By adding more and more different atom types to a crystal, you can generate more and more disorder if the arrangement of atoms on that lattice remains random. Finding the right mix of atoms that will retain this randomly mixed state is the key to entropy stabilization and testing the entropy question.
In this case, researchers created an entropy-stabilized material made up of five different oxides in roughly equal amounts: magnesium oxide, cobalt oxide, nickel oxide, copper oxide and zinc oxide. The individual materials were mixed in powder form, pressed into a small pellet, then heat treated at 1000 degrees Celsius for several days to promote reaction and mixing.
The researchers then used the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory and X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy to determine that the constituent atoms in the entropy-stabilized oxide were evenly distributed and that their placement in the crystalline lattice structure was random.
"The spectroscopy told us that each unit cell in the entropy-stabilized oxide's structure had the appropriate distribution of atoms, but that where each atom was located in a unit cell was random," Maria says. "Making this determination is very difficult, and requires the most sophisticated characterization tools available at the Advanced Photon Source.
"This is fascinating - we've proved that you can create entirely new crystalline phases of matter - but it's fundamental research," Maria says. "A lot of additional work needs to be done to characterize the properties of these materials and what the potential applications may be.
"However, the work does tell us that we'll be able to engineer new materials in unusual ways - and that is very promising for developing materials with desirable properties."
###
The paper, "Entropy-Stabilized Oxides," will be published online Sept. 29 in Nature Communications. Lead author of the paper is NC State Ph.D. student Christina Rost. The paper was co-authored by Edward Sachet, Trent Borman, Ali Moballegh, Elizabeth Dickey, Dong Hou and Jacob Jones of NC State; and by Stefano Curtarolo of Duke University.
The research was supported by the U.S. Army Research Office under grant number W911NF-14-0285 and the National Science Foundation under grant number EEC 1156762.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








