Home > Press > Wearable electronic health patches may now be cheaper and easier to make
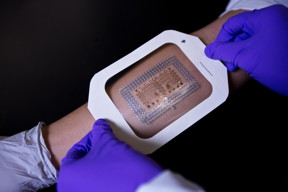 |
| Cockrell School of Engineering assistant professor Nanshu Lu and her team have developed a low-cost, faster method for making epidermal electronics. CREDIT: Cockrell School of Engineering |
Abstract:
A team of researchers in the Cockrell School of Engineering at The University of Texas at Austin has invented a method for producing inexpensive and high-performing wearable patches that can continuously monitor the body's vital signs for human health and performance tracking, potentially outperforming traditional monitoring tools such as cardiac event monitors.
Wearable electronic health patches may now be cheaper and easier to make
Austin, TX | Posted on September 30th, 2015The researchers published a paper on their patent-pending process in Advanced Materials on Sept. 23.
Led by Assistant Professor Nanshu Lu, the team's manufacturing method aims to construct disposable tattoo-like health monitoring patches for the mass production of epidermal electronics, a popular technology that Lu helped develop in 2011.
The team's breakthrough is a repeatable "cut-and-paste" method that cuts manufacturing time from several days to only 20 minutes. The researchers believe their new method is compatible with roll-to-roll manufacturing -- an existing method for creating devices in bulk using a roll of flexible plastic and a processing machine.
Reliable, ultrathin wearable electronic devices that stick to the skin like a temporary tattoo are a relatively new innovation. These devices have the ability to pick up and transmit the human body's vital signals, tracking heart rate, hydration level, muscle movement, temperature and brain activity.
Although it is a promising invention, a lengthy, tedious and costly production process has until now hampered these wearables' potential.
"One of the most attractive aspects of epidermal electronics is their ability to be disposable," Lu said. "If you can make them inexpensively, say for $1, then more people will be able to use them more frequently. This will open the door for a number of mobile medical applications and beyond."
The UT Austin method is the first dry and portable process for producing these electronics, which, unlike the current method, does not require a clean room, wafers and other expensive resources and equipment. Instead, the technique relies on freeform manufacturing, which is similar in scope to 3-D printing but different in that material is removed instead of added.
The two-step process starts with inexpensive, pre-fabricated, industrial-quality metal deposited on polymer sheets. First, an electronic mechanical cutter is used to form patterns on the metal-polymer sheets. Second, after removing excessive areas, the electronics are printed onto any polymer adhesives, including temporary tattoo films. The cutter is programmable so the size of the patch and pattern can be easily customized.
Deji Akinwande, an associate professor and materials expert in the Cockrell School, believes Lu's method can be transferred to roll-to-roll manufacturing.
"These initial prototype patches can be adapted to roll-to-roll manufacturing that can reduce the cost significantly for mass production," Akinwande said. "In this light, Lu's invention represents a major advancement for the mobile health industry."
After producing the cut-and-pasted patches, the researchers tested them as part of their study. In each test, the researchers' newly fabricated patches picked up body signals that were stronger than those taken by existing medical devices, including an ECG/EKG, a tool used to assess the electrical and muscular function of the heart. The team also found that their patch conforms almost perfectly to the skin, minimizing motion-induced false signals or errors.
The UT Austin wearable patches are so sensitive that Lu and her team can envision humans wearing the patches to more easily maneuver a prosthetic hand or limb using muscle signals. For now, Lu said, "We are trying to add more types of sensors including blood pressure and oxygen saturation monitors to the low-cost patch."
###
This research was funded by NSF grants, including Lu's NSF CAREER grant.
The University of Texas at Austin is committed to transparency and disclosure of all potential conflicts of interest. The university investigator who led this research, Nanshu Lu, has submitted required financial disclosure forms with the university. Lu is co-founder and scientific adviser for Stretch Med Inc., a medical device company in which she has an equity partnership. Stretch Med is developing human electrophysiological sensors for clinical use, drawing on some of the patent-pending technologies described in this release.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sandra Zaragoza
512-471-2129
Copyright © University of Texas at Austin
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Flexible Electronics
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








