Home > Press > A new single-molecule tool to observe enzymes at work
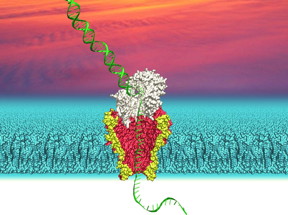 |
| This is an illustration of a nanopore derived from a genetically modified bacterial membrane channel with DNA passing through it. CREDIT: Ian Derrington, University of Washington |
Abstract:
A team of scientists at the University of Washington and the biotechnology company Illumina have created an innovative tool to directly detect the delicate, single-molecule interactions between DNA and enzymatic proteins. Their approach provides a new platform to view and record these nanoscale interactions in real time. As they report Sept. 28 in Nature Biotechnology, this tool should provide fast and reliable characterization of the different mechanisms cellular proteins use to bind to DNA strands -- information that could shed new light on the atomic-scale interactions within our cells and help design new drug therapies against pathogens by targeting enzymes that interact with DNA.
A new single-molecule tool to observe enzymes at work
Seattle, WA | Posted on September 28th, 2015"There are other single-molecule tools around, but our new tool is far more sensitive," said senior author and UW physics professor Jens Gundlach. "We can really pick up atomic-scale movements that a protein imparts onto DNA."
As can happen in the scientific process, they developed this tool -- the single-molecule picometer-resolution nanopore tweezers, or SPRNT -- while working on a related project.
The UW team has been exploring nanopore technology to read DNA sequences quickly. Our genes are long stretches of DNA molecules, which are made up of combinations of four chemical DNA "letters." In their approach, Gundlach and his team measure an electrical current through a biological pore called MspA, which is embedded within a modified cell membrane. As DNA passes through a tiny opening in the pore -- an opening that is just 0.00000012 centimeters wide, or 1/10,000th the width of a human hair -- the current shifts based on the sequence of DNA letters. They use these changes in current to infer DNA sequences.
Gundlach and his team, in the process of investigating nanopore sequencing, tried out a variety of molecular motors to move DNA through the pore. They discovered that their experimental setup was sensitive enough to observe motions much smaller than the distance between adjacent letters on the DNA. As they report in their paper, SPRNT is more than seven times more sensitive than existing techniques to measure interactions between DNA and proteins.
"Generally, most existing techniques to look at single-molecule movements -- such as optical tweezers -- have a resolution, at best, of about 300 picometers," said Gundlach. "With SPRNT, we can have 40 picometer resolution."
For reference, 40 picometers are 0.000000004 centimeters, or about 0.0000000016 inches.
"We realized we can detect minute differences in the position of the DNA in the pore," said UW physics postdoctoral researcher Andrew Laszlo, a co-author on the paper. "We could pick up differences in how the proteins were binding to DNA and moving it through the pore."
These differences account for the unique role each cellular protein plays as it interacts with DNA. Cells have proteins to copy DNA, "read" DNA to express genes and repair DNA when it is damaged. There are cellular proteins that unwind DNA, while others bunch DNA tightly together.
Biologists have long recognized that proteins have different structures to perform these roles, but the physical motion of proteins as they work on DNA has been difficult to detect directly.
"When you have the kind of resolution that SPRNT offers, you can start to pick apart the minute steps these proteins take," said Laszlo.
Gundlach and his team show that SPRNT is sensitive enough to differentiate between the mechanisms that two cellular proteins use to pass DNA through the nanopore opening. One protein, which normally copies DNA, moves along the DNA one letter at a time as it guides DNA through the pore. The second protein, which normally unwinds DNA, instead takes two steps along each DNA letter, which they could pick up by tracking minute changes in the current, according to co-author and UW physics doctoral student Jonathan Craig. They even discovered that these two steps involve sequential chemical processes that the protein uses to walk along DNA.
"You can really see the underlying mechanisms, and that has a ton of implications -- from understanding how life works to drug design," said Laszlo.
Gundlach believes this tool may open a new window for understanding how cellular proteins process DNA, which could help genetically engineer proteins to perform novel jobs. These fine details may also help scientists understand how mutations in proteins can lead to disease or find protein properties that would be ideal targets for drug therapies.
"For example, viral genes code for their own proteins that process their DNA," said Gundlach. "If we can use SPRNT to screen for drugs that specifically disrupt the functioning of these proteins, it may be possible to interfere with viruses."
###
Other UW authors on the paper include lead author Ian Derrington, a postdoctoral researcher in physics, and Brian Ross, Henry Brinkerhoff, Ian Nova, Kenji Doering and Benjamin Tickman. Co-authors at Illumina are Kevin Gunderson, Eric Stava, Mostafa Ronaghi and Jeffrey Mandell. Gundlach's laboratory received funding for this project from the National Institutes of Health's $1,000 Genome Project, grant number R01HG005115.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
James Urton
206-543-2580
Jens Gundlach
206-543-8774
Copyright © University of Washington
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








