Home > Press > UCLA physicists determine 3-D positions of individual atoms for the first time: Finding will help scientists better understand the structural properties of materials
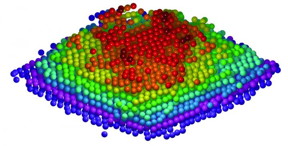 |
| The 3-D coordinates of thousands of individual atoms and a point defect in a material were determined with a precision of 19 trillionths of a meter, where the crystallinity of the material is not assumed. The figure shows the measured 3-D atomic positions of a tungsten tip, consisting of nine atomic layers, labeled with crimson (dark red), red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, blue, magenta and purple from layers one (top) to nine (bottom), respectively. CREDIT: Mary Scott and Jianwei (John) Miao/UCLA |
Abstract:
Atoms are the building blocks of all matter on Earth, and the patterns in which they are arranged dictate how strong, conductive or flexible a material will be. Now, scientists at UCLA have used a powerful microscope to image the three-dimensional positions of individual atoms to a precision of 19 trillionths of a meter, which is several times smaller than a hydrogen atom.
UCLA physicists determine 3-D positions of individual atoms for the first time: Finding will help scientists better understand the structural properties of materials
Los Angeles, CA | Posted on September 21st, 2015Their observations make it possible, for the first time, to infer the macroscopic properties of materials based on their structural arrangements of atoms, which will guide how scientists and engineers build aircraft components, for example. The research, led by Jianwei (John) Miao, a UCLA professor of physics and astronomy and a member of UCLA's California NanoSystems Institute, is published Sept. 21 in the online edition of the journal Nature Materials.
For more than 100 years, researchers have inferred how atoms are arranged in three-dimensional space using a technique called X-ray crystallography, which involves measuring how light waves scatter off of a crystal. However, X-ray crystallography only yields information about the average positions of many billions of atoms in the crystal, and not about individual atoms' precise coordinates.
"It's like taking an average of people on Earth," Miao said. "Most people have a head, two eyes, a nose and two ears. But an image of the average person will still look different from you and me."
Because X-ray crystallography doesn't reveal the structure of a material on a per-atom basis, the technique can't identify tiny imperfections in materials such as the absence of a single atom. These imperfections, known as point defects, can weaken materials, which can be dangerous when the materials are components of machines like jet engines.
"Point defects are very important to modern science and technology," Miao said.
Miao and his team used a technique known as scanning transmission electron microscopy, in which a beam of electrons smaller than the size of a hydrogen atom is scanned over a sample and measures how many electrons interact with the atoms at each scan position. The method reveals the atomic structure of materials because different arrangements of atoms cause electrons to interact in different ways.
However, scanning transmission electron microscopes only produce two-dimensional images. So creating a 3-D picture requires scientists to scan the sample once, tilt it by a few degrees and re-scan it -- repeating the process until the desired spatial resolution is achieved -- before combining the data from each scan using a computer algorithm. The downside of this technique is that the repeated electron beam radiation can progressively damage the sample.
Using a scanning transmission electron microscope at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory's Molecular Foundry, Miao and his colleagues analyzed a small piece of tungsten, an element used in incandescent light bulbs. As the sample was tilted 62 times, the researchers were able to slowly assemble a 3-D model of 3,769 atoms in the tip of the tungsten sample.
The experiment was time consuming because the researchers had to wait several minutes after each tilt for the setup to stabilize.
"Our measurements are so precise, and any vibrations -- like a person walking by -- can affect what we measure," said Peter Ercius, a staff scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and an author of the paper.
The researchers compared the images from the first and last scans to verify that the tungsten had not been damaged by the radiation, thanks to the electron beam energy being kept below the radiation damage threshold of tungsten.
Miao and his team showed that the atoms in the tip of the tungsten sample were arranged in nine layers, the sixth of which contained a point defect. The researchers believe the defect was either a hole in an otherwise filled layer of atoms or one or more interloping atoms of a lighter element such as carbon.
Regardless of the nature of the point defect, the researchers' ability to detect its presence is significant, demonstrating for the first time that the coordinates of individual atoms and point defects can be recorded in three dimensions.
"We made a big breakthrough," Miao said.
Miao and his team plan to build on their results by studying how atoms are arranged in materials that possess magnetism or energy storage functions, which will help inform our understanding of the properties of these important materials at the most fundamental scale.
"I think this work will create a paradigm shift in how materials are characterized in the 21st century," he said. "Point defects strongly influence a material's properties and are discussed in many physics and materials science textbooks. Our results are the first experimental determination of a point defect inside a material in three dimensions."
###
The study's co-authors include Rui Xu, Chien-Chun Chen, Li Wu, Mary Scott, Matthias Bartels, Yongsoo Yang and Michael Sawaya, all of UCLA; as well as Colin Ophus of Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; Wolfgang Theis of the University of Birmingham; Hadi Ramezani-Dakhel and Hendrik Heinz of the University of Akron; and Laurence Marks of Northwestern University.
This work was primarily supported by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Basic Energy Sciences (grant DE-FG02-13ER46943 and contract DE-AC02--05CH11231).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Stuart Wolpert
310-206-0511
Copyright © UCLA
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








