Home > Press > Science provides new way to peer into pores: Rice University lab finds technique to characterize nanoscale spaces in porous materials
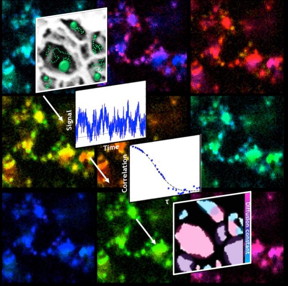 |
| The paths fluorescent particles take as they diffuse through a porous nanoscale structure reveal the arrangement of the pores through a technique developed by scientists at Rice University. CREDIT: Landes Research Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
Rice University scientists led a project to "see" and measure the space in porous materials, even if that space is too small or fragile for traditional microscopes.
Science provides new way to peer into pores: Rice University lab finds technique to characterize nanoscale spaces in porous materials
Houston, TX | Posted on September 9th, 2015The Rice lab of chemist Christy Landes invented a technique to characterize such nanoscale spaces, an important advance toward her group's ongoing project to efficiently separate "proteins of interest" for drug manufacture. It should also benefit the analysis of porous materials of all kinds, like liquid crystals, hydrogels, polymers and even biological substances like cytosol, the compartmentalized fluids in cells.
The research with collaborators at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and Kansas State University appears in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano.
It's easy to use a fluorescent chemical compound to tag, or "label," a material and take a picture of it, Landes said. "But what if the thing you want a picture of is mostly nothing? That's the problem we had to solve to understand what was going on in the separation material."
The team aims to improve protein separation in a process called chromatography, in which solutions flow through porous material in a column. Because different materials travel at different speeds, the components separate and can be purified.
"We learned that in agarose, a porous material used to separate proteins, the clustering of charges is very important," Landes said. While the protein project succeeded, "when we matched experimental data to our theory, there was something additional contributing to the separation that we couldn't explain."
The answer appeared to be with how charged particles like nanoscale ligands arranged themselves in the pores. "It was the only possible explanation," Landes said. "So we needed a way to image the pores."
Standard techniques like atomic force, X-ray and electron microscopy would require samples to be either frozen or dried. "That would either shrink or swell or change their structures," she said.
It occurred to the team to combine their experience with the Nobel Prize-winning super-resolution microscopy and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy techniques. Super-resolution microscopy is a way to see objects at resolutions below the diffraction limit, which restricts the viewing of things that are smaller than the wavelength of light directed at them.
Correlation spectroscopy is a way to measure fluorescent particles as they fluctuate. By crunching data collected via a combination of super-resolution microscopy and correlation spectroscopy, the researchers mapped slices of the material to see where charged particles tended to cluster.
The combined technique, which they call fcsSOFI (for "fluorescence correlation spectroscopy super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging"), measures fluorescent tags as they diffuse in the pores, which allows researchers to simultaneously characterize dimensions and dynamics within the pores. The lab tested its technique on both soft agarose hydrogels and lyotropic liquid crystals. Next, they plan to extend their mapping to three-dimensional spaces.
"We now have both pieces of our puzzle: We can see our proteins interacting with charges within our porous material, and we can measure the pores," Landes said. "This has direct relevance to the protein separation problem for the $100 billion pharmaceutical industry."
###
Co-authors of the paper are Rice alumnus Lydia Kisley and Rice graduate students Lawrence Tauzin and Bo Shuang; Rice Quantum Institute/Smalley-Curl Institute summer undergraduate student Rachel Brunetti of Scripps College, Claremont, Calif.; graduate student Xiyu Yi and Shimon Weiss, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry, at UCLA; and graduate student Alec Kirkeminde and Daniel Higgins, a professor of chemistry, at Kansas State.
The Welch Foundation, the National Science Foundation, the Willard Chair at UCLA and the Department of Energy supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,888 undergraduates and 2,610 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
Hydrogels
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








