Home > Press > Rice researchers demo solar water-splitting technology: Process uses light-harvesting nanoparticles, captures energy from 'hot electrons'
 |
| Rice University researchers have demonstrated an efficient new way to capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into clean, renewable energy by splitting water molecules. CREDIT: I. Thomann/Rice University |
Abstract:
Rice University researchers have demonstrated an efficient new way to capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into clean, renewable energy by splitting water molecules.
Rice researchers demo solar water-splitting technology: Process uses light-harvesting nanoparticles, captures energy from 'hot electrons'
Houston, TX | Posted on September 5th, 2015The technology, which is described online in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters, relies on a configuration of light-activated gold nanoparticles that harvest sunlight and transfer solar energy to highly excited electrons, which scientists sometimes refer to as "hot electrons."
"Hot electrons have the potential to drive very useful chemical reactions, but they decay very rapidly, and people have struggled to harness their energy," said lead researcher Isabell Thomann, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering and of chemistry and materials science and nanoengineering at Rice. "For example, most of the energy losses in today's best photovoltaic solar panels are the result of hot electrons that cool within a few trillionths of a second and release their energy as wasted heat."
Capturing these high-energy electrons before they cool could allow solar-energy providers to significantly increase their solar-to-electric power-conversion efficiencies and meet a national goal of reducing the cost of solar electricity.
In the light-activated nanoparticles studied by Thomann and colleagues at Rice's Laboratory for Nanophotonics (LANP), light is captured and converted into plasmons, waves of electrons that flow like a fluid across the metal surface of the nanoparticles. Plasmons are high-energy states that are short-lived, but researchers at Rice and elsewhere have found ways to capture plasmonic energy and convert it into useful heat or light. Plasmonic nanoparticles also offer one of the most promising means of harnessing the power of hot electrons, and LANP researchers have made progress toward that goal in several recent studies.
Thomann and her team, graduate students Hossein Robatjazi, Shah Mohammad Bahauddin and Chloe Doiron, created a system that uses the energy from hot electrons to split molecules of water into oxygen and hydrogen. That's important because oxygen and hydrogen are the feedstocks for fuel cells, electrochemical devices that produce electricity cleanly and efficiently.
To use the hot electrons, Thomann's team first had to find a way to separate them from their corresponding "electron holes," the low-energy states that the hot electrons vacated when they received their plasmonic jolt of energy. One reason hot electrons are so short-lived is that they have a strong tendency to release their newfound energy and revert to their low-energy state. The only way to avoid this is to engineer a system where the hot electrons and electron holes are rapidly separated from one another. The standard way for electrical engineers to do this is to drive the hot electrons over an energy barrier that acts like a one-way valve. Thomann said this approach has inherent inefficiencies, but it is attractive to engineers because it uses well-understood technology called Schottky barriers, a tried-and-true component of electrical engineering.
"Because of the inherent inefficiencies, we wanted to find a new approach to the problem," Thomann said. "We took an unconventional approach: Rather than driving off the hot electrons, we designed a system to carry away the electron holes. In effect, our setup acts like a sieve or a membrane. The holes can pass through, but the hot electrons cannot, so they are left available on the surface of the plasmonic nanoparticles."
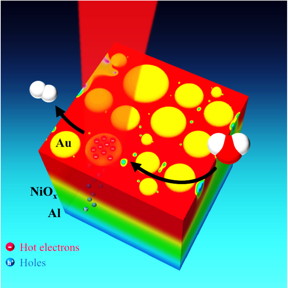
The setup features three layers of materials. The bottom layer is a thin sheet of shiny aluminum. This layer is covered with a thin coating of transparent nickel-oxide, and scattered atop this is a collection of plasmonic gold nanoparticles -- puck-shaped disks about 10 to 30 nanometers in diameter.
When sunlight hits the discs, either directly or as a reflection from the aluminum, the discs convert the light energy into hot electrons. The aluminum attracts the resulting electron holes and the nickel oxide allows these to pass while also acting as an impervious barrier to the hot electrons, which stay on gold. By laying the sheet of material flat and covering it with water, the researchers allowed the gold nanoparticles to act as catalysts for water splitting. In the current round of experiments, the researchers measured the photocurrent available for water splitting rather than directly measuring the evolved hydrogen and oxygen gases produced by splitting, but Thomann said the results warrant further study.
"Utilizing hot electron solar water-splitting technologies we measured photocurrent efficiencies that were on par with considerably more complicated structures that also use more expensive components," Thomann said. "We are confident that we can optimize our system to significantly improve upon the results we have already seen."
Robatjazi is a graduate student in electrical and computer engineering, Bahauddin is a graduate student in physics and astronomy and Doiron is a graduate student in applied physics. The research was supported by the Welch Foundation and a National Science Foundation CAREER Award.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nationís top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,888 undergraduates and 2,610 graduate students, Riceís undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplingerís Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations on Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Jade Boyd
713-348-6778
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() A copy of the NanoLetters paper, "Direct Plasmon-Driven Photoelectrocatalysis," is available at:
A copy of the NanoLetters paper, "Direct Plasmon-Driven Photoelectrocatalysis," is available at:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








