Home > Press > Magnetic wormhole connecting 2 regions of space created for the first time: The device could have applications in medicine, opening up ways to make MRIs more comfortable for patients
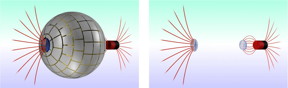 |
| (Left) 3-D diagram of the magnetic wormhole shows how the magnetic field lines (in red) leaves a magnet on the right pass through the wormhole. (Right) In terms of magnetism the wormhole is undetectable, which means that the magnetic field seems to disappear on the right only to reappear on the left in the form of a magnetic monopole. CREDIT: Jordi Prat-Camps and Universitat Autňnoma de Barcelona; the figure may be used in the media. |
Abstract:
"Wormholes" are cosmic tunnels that can connect two distant regions of the universe, and have been popularised by the dissemination of theoretical physics and by works of science fiction like Stargate, Star Trek or, more recently, Interstellar. Using present-day technology it would be impossible to create a gravitational wormhole, as the field would have to be manipulated with huge amounts of gravitational energy, which no-one yet knows how to generate. In electromagnetism, however, advances in metamaterials and invisibility have allowed researchers to put forward several designs to achieve this.
Magnetic wormhole connecting 2 regions of space created for the first time: The device could have applications in medicine, opening up ways to make MRIs more comfortable for patients
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on September 4th, 2015Scientists in the Department of Physics at the Universitat Autňnoma de Barcelona have designed and created in the laboratory the first experimental wormhole that can connect two regions of space magnetically. This consists of a tunnel that transfers the magnetic field from one point to the other while keeping it undetectable - invisible - all the way.
The researchers used metamaterials and metasurfaces to build the tunnel experimentally, so that the magnetic field from a source, such as a magnet or a an electromagnet, appears at the other end of the wormhole as an isolated magnetic monopole. This result is strange enough in itself, as magnetic monopoles - magnets with only one pole, whether north or south - do not exist in nature. The overall effect is that of a magnetic field that appears to travel from one point to another through a dimension that lies outside the conventional three dimensions.
The wormhole in this experiment is a sphere made of different layers: an external layer with a ferromagnetic surface, a second inner layer, made of superconducting material, and a ferromagnetic sheet rolled into a cylinder that crosses the sphere from one end to the other. The sphere is made in such a way as to be magnetically undetectable - invisible, in magnetic field terms - from the exterior.
The magnetic wormhole is an analogy of gravitational ones, as it "changes the topology of space, as if the inner region has been magnetically erased from space", explains Ŕlvar Sánchez, the lead researcher.
These same researchers had already built a magnetic fibre in 2014: a device capable of transporting the magnetic field from one end to the other. This fibre was, however, detectable magnetically. The wormhole developed now, though, is a completely three-dimensional device that is undetectable by any magnetic field.
This means a step forward towards possible applications in which magnetic fields are used: in medicine for example. This technology could, for example, increase patients' comfort by distancing them from the detectors when having MRI scans in hospital, or allow MRI images of different parts of the body to be obtained simultaneously.
###
This study, published in Scientific Reports, involved the UAB Department of Physics researchers Jordi Prat, Carles Navau and Ŕlvar Sánchez, who is also a lecturer at ICREA Academy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ŕlvar Sánchez
Copyright © Universitat Autňnoma de Barcelona
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








