Home > Press > Draw out of the predicted interatomic force
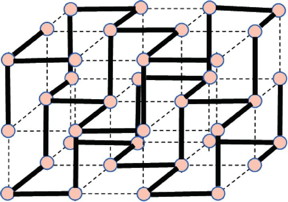 |
| This is a schematic picture using simple cubic lattice, where bold and broken lines denote short strong bonds and long weak ones, respectively. CREDIT: M. Inui, Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University, et al. |
Abstract:
Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Liquid Bi shows a peculiar dispersion of the acoustic mode, which is related to the Peierls distortion in the crystalline state. These results will provide valuable inspiration to researchers developing new materials in the nanotechnology field.
Draw out of the predicted interatomic force
Hiroshima, Japan | Posted on August 30th, 2015Studies of the atomic dynamics in liquid Bi have been revisited more recently. The previous inelastic neutron scattering (INS) results for liquid Bi showed inconsistency for the inelastic excitation of the acoustic mode. These results were also different from the ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) prediction that indicated that the peculiar atomic dynamics arose from an anisotropic interatomic force in this monatomic liquid [1].
Therefore, it is important to observe the inelastic excitation of the acoustic mode in liquid Bi using inelastic x-ray scattering (IXS).
Professor M. Inui at Hiroshima University and his collaborators at Kumamoto University, Keio University, SPring-8/JASRI, and the RIKEN SPring-8 Center measured the IXS on liquid Bi at SPring-8 [2]. This research group found that the dispersion curve of the excitation energy of the acoustic mode exhibits a flat region as a function of the momentum transfer.
The experiments conducted by Professor Inui et al. used a single-crystal sapphire cell of the Tamura type that was carefully machined to provide a 0.04-mm sample thickness.
It is said that only his research group can make full use of this "world-famous" cell, which was used to stably conduct an x-ray beam experiment under high temperatures.
Furthermore, this research group reported that the IXS experimental results for liquid Bi clearly show a distinct inelastic excitation of the acoustic mode. This resolves the previous disagreement in the literature. Those researchers said, "Consistent with ab initio calculations of liquid Bi[1], the dispersion curve was nearly flat from 7 to 15 nm [to the negative 1 power]."
They also mentioned, "A long-range force is needed to reproduce the flatness of the dispersion curve, and the long-range force has to strongly be related to a local structure consisting of shorter and longer bounds in the liquid."
This research group demonstrated a possible mechanism for the unusual dispersion of liquid Bi. Their results will greatly contribute to the development of nanotechnology.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Norifumi Miyokawa
Copyright © Hiroshima University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








