Home > Press > Novel nanostructures for efficient long-range energy transport
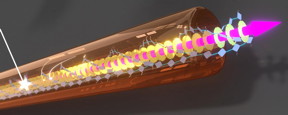 |
| This is a supramolecular nanofiber consisting of more than 10,000 perfectly ordered building blocks, which enables an energy transport over a distance of more than 4 micrometers at room temperature. CREDIT: Picture by A. T. Haedler. |
Abstract:
The conversion of sunlight into electricity at low cost becomes increasingly important to meet the world's fast growing energy consumption. This task requires the development of new device concepts, in which particularly the transport of light-generated energy with minimal losses is a key aspect. An interdisciplinary group of researchers from the Universities of Bayreuth and Erlangen-Nuremberg (Germany) report in Nature on nanofibers, which enable for the first time a directed energy transport over several micrometers at room temperature. This transport distance can only be explained with quantum coherence effects along the individual nanofibers.
Novel nanostructures for efficient long-range energy transport
Bayreuth, Germany | Posted on August 21st, 2015The research groups of Richard Hildner (Experimental Physics) and Hans-Werner Schmidt (Macromolecular Chemistry) at the University of Bayreuth prepared supramolecular nanofibers, which can comprise more than 10,000 identical building blocks. The core of the building block is a so-called carbonyl-bridged triarylamine. This triarylamine derivative was synthesized by the research group of Milan Kivala (Organic Chemistry) at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg and chemically modified at the University of Bayreuth. Three naphthalimidbithiophene chromophores are linked to this central unit. Under specific conditions, the building blocks spontaneously self-assemble and form nanofibers with lengths of more than 4 micrometers and diameters of only 0.005 micrometer. For comparison: a human hair has a thickness of 50 to 100 micrometers.
With a combination of different microscopy techniques the scientists at the University of Bayreuth were able to visualize the transport of excitation energy along these nanofibers. To achieve this long-range energy transport, the triarylamine cores of the building blocks, that are perfectly arranged face to face, act in concert. Thus, the energy can be transferred in a wave-like manner from one building block to the next: This phenomenon is called quantum coherence.
"These highly promising nanostructures demonstrate that carefully tailoring materials for the efficient transport of light energy is an emerging research area" says Dr. Richard Hildner, an expert in the field of light harvesting at the University of Bayreuth. The research area light harvesting aims at a precise description of the transport processes in natural photosynthetic machineries to use this knowledge for building novel nanostructures for power generation from sunlight. In this field interdisciplinary groups of researchers work together in the Bavarian initiative Solar Technologies Go Hybrid and in the Research Training Group Photophysics of synthetic and biological multichromophoric systems (GRK 1640) funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG).
###
Publication:
Andreas T. Haedler et al.: Long-Range Energy Transport in Single Supramolecular Nanofibres at Room Temperature,
Nature 523, 196 - 199 (2015), DOI: 10.1038/nature14570.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Richard Hildner
Experimental Physics IV
University of Bayreuth
Phone: +49 (0) 921 55 4040
Prof. Dr. Hans-Werner Schmidt
Macromolecular Chemistry I
University of Bayreuth
Phone: +49 (0) 921 55 3200 und -3299
Copyright © University of Bayreuth
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








