Home > Press > Cave snail from South Korea suggests ancient subterranean diversity across Eurasia
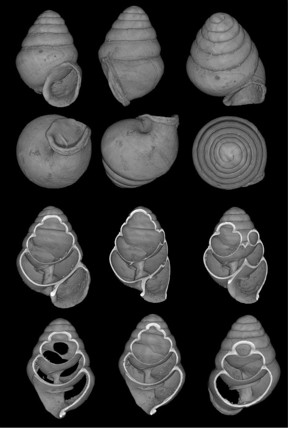 |
| This image shows inside and outside views of Koreozospeum nodongense holotype.
Credit: Dr. Adrienne Jochum |
Abstract:
As tiny as 1.7 mm, a snail whose relatives live exclusively in the deep recesses of caves, provided a sensational discovery from the depths of Nodong cave, South Korea, back in 2000 for its collector, J. S. Lee. It is the only cave-dwelling representative of the family of hollow-shelled snails in the whole of Asia with its closest relatives known from as far as Croatia and Northern Spain. The scientists, Adrienne Jochum, Bern University and Natural History Museum Bern, Larisa Prozorova and Mariana Sharyiool from the Far Eastern Russian Academy of Sciences and Barna Páll-Gergely from Shinshu University, published its description in the open-access journal ZooKeys.
Cave snail from South Korea suggests ancient subterranean diversity across Eurasia
Sofia, Bulgaria | Posted on August 18th, 2015The Asian species has awaited 15 years to come out of the dark for a name and into the limelight of subterranean biodiversity and conservation awareness. This barely visible snail suggests a former pan-Eurasian distribution of cave-dwelling, hollow-spired snails.
The tiny-shelled treasure, called Koreozospeum nodongense, belongs to a larger group of ancient cosmopolitan air-breathing relatives known to have been amongst the first snail colonisers of land via mangroves about 65 million years ago. Similar to its European relatives from the genus Zospeum, the South Korean snail was also found on muddy cave walls.
Although more than 1,000 caves have been explored in South Korea, Nodong is so far the only one to harbour these beautiful denizens of the dark. Hypotheses made by Culver et. al. in 2006 about the existence of a very narrow, mid-latitudinal ridge of subterranean biodiversity (ca. 42-46°N in Europe and 33-35°N in North America) might clarify this unique find.
A high amount of caves known to exist within these latitudes provide ample habitats for colonisation of life. If this hypothetical ridge were to be extended further East away from Europe, then Koreozopseum's gliding along walls in a South Korean cave (33-35°N) makes a strong call for further investigations and discovery of rare biodiversity.
Jochum and her international team described K. nodongense using computer tomographic scans (Nano-CT) in a video film to view and compare the contours and architecture of the very fragile shell. Chemical trace elements, such as aluminum (Al) and silicon (Si) were detected in other scans of the thin diaphanous shell using mineralogical analysis techniques (SEM-EDX). These elements may play a role in the biomineralization (hardness) of the shell or may be contaminants absorbed by the snail from sediment consisting of volcanic ash from former eruptions in the region.
Additional information:
The Naturhistorisches Museum der Burgergemeinde Bern, Switzerland and the Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences supported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Adrienne Jochum
Copyright © Pensoft Publishers
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








